Blockchain, the technology developed to enable the crypto-currency Bitcoin has become the latest big buzz phrase technology across industries worldwide, but is it just hyperbole or can it be an important factor in the future of field service?
ARCHIVE FOR THE ‘future-of-field-service’ CATEGORY
Apr 12, 2018 • Features • 3D printing • 3DToken • Coin Telegraph • Computer Weekly • crypto currency • Future of FIeld Service • Joseph Pindar • Malware • Mirai • bitcoin • Blockchain • Cyber Security • Gemalto • IoT • Satoshi Nakamoto • service supply chain • Parts Pricing and Logistics
Blockchain, the technology developed to enable the crypto-currency Bitcoin has become the latest big buzz phrase technology across industries worldwide, but is it just hyperbole or can it be an important factor in the future of field service?
Business across the world are turning their attention to BlockChain right now and in the majority of cases, the main focus of this attention is centred around Bitcoin, the first globally recognized digital (crypto) currency that has hit the headlines largely for huge spikes and dips in its value across the last 12 months.
However, whilst Crypto-Currency is the most widely understood application of Blockchain technology, there may be a number of other applications which could be far more important to how the field service sector operates.
Blockchain 101
So for the uninitiated lets first get our heads around exactly what BlockChain is...
To begin a blockchain is a continuously growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked and secured using encrypted codes. Essentially, each block will typically contain a cryptographic hash of the previous block, alongside a time stamp and the transaction data.
Perhaps the most critical point to comprehend about blockchain is that by design, a blockchain is inherently resistant to modification of the dataPerhaps the most critical point to comprehend about blockchain is that by design, a blockchain is inherently resistant to modification of the data. The technical language is that it is “an open, distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way”.
When used as a distributed ledger, a blockchain is generally managed by a peer-to-peer network which adheres to the same protocols for validating new blocks collectively. What this means is that in practice, once the data is within in any given block it can not be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks. The particularly clever part here is that as each peer within the chain is working as part of the collective, such a change requires the collusion of a majority from the network - this makes pulling a fast one anywhere along the line pretty much near impossible.
Thus blockchains are inherently secure by design.
For the more technically minded amongst us, one could suggest quite rightly that the establishment of blockchain has meant that decentralized consensus has become realized, with blockchain ‘exemplifying a distributed computing system with high Byzantine fault tolerance’
For those of us who are perhaps more interested in the outcomes, however, essentially what we need to know is that due to the way they have been designed they are highly suitable for the recording of information that needs watertight security - such as medical records and of course financial transactions - which is where it all began.
Whilst Blockchain is rapidly gaining attention, it is the crypto-currency that it was created for use with, Bitcoins, even more widely recognized within the mainstream.
Blockchain was invented by wonderfully mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto back in 2008 as Bitcoin’s public transaction ledger.
Indeed it was the invention of the blockchain that allowed bitcoin to become the first digital currency to solve what is known as the ‘double spending problem’, without the need of a trusted authority or central server - essentially making crypto-currency viable.
So it’s just a new way of taking payment?
Well no, as we alluded to at the top there could be a lot more to how Blockchain plays a role in field service which we’ll go into shortly - but whilst we are at it there is certainly a case for adding crypto-currencies to the list of how your organisation receives payment for the services delivered - especially if you are serving the consumer directly.
Certainly whilst crypto-currency is by no means a mainstream payment method as yet, an increasing number of businesses are starting to accept it and with a lower barrier to entry than accepting plastic, any business in any industry has the ability to adopt crypto-currencies.
In Japan alone, an estimated 260,000 businesses were reported to offer the cryptocurrency as a payment channel in 2017.In Japan alone, an estimated 260,000 businesses were reported to offer the cryptocurrency as a payment channel in 2017.
But what are the benefits of accepting cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin for a business?
There are plenty of positives in doing so but some key reasons cited in an article on business.com include:
- Eliminate chargeback fraud: A Bitcoin transaction is immutable. Once a client has paid for a product or service, the money is in your account. Unlike credit card payments, charges cannot be reversed.
- Immediate availability: There is no third party-dependent waiting period the way there is with bank-owned payments.Once payment is successful, the transaction amount is in your wallet and accessible immediately.You can convert Bitcoin into your local currency fiat at the end of each transaction, at the end of each working day or according to a custom set schedule.
- Lower transaction costs: Credit card payments usually end up costing you a 2 to 4 percent fee.With Bitcoin, this amount is a low flat fee, not a percentage of the transaction.
- Attract new customers: As Bitcoin rises in popularity, more users seek out participating businesses. This can mean exposure to a clientele you didn’t have before.
- Garner publicity: Bitcoin makes the news in a way fiat currency can’t. Local, national and even international news outlets are reporting on businesses taking Bitcoin payments, giving you an opportunity for free publicity.
Fixing the holes in the Internet of Things
However, as mentioned above, within the field service sector Blockchain has a huge amount more potential than just facilitating an additional means of receiving payment.
Firstly, there is its potential application within the Internet of Things - which is set to become the fundamental backbone of service delivery in the future - although widespread mass adoption is still arguably held back due to security concerns, a very real example of which being realized back in October 2016 when an unprecedented distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack involving an estimated 100,000 compromised devices in the Mirai malware botnet nearly brought the Internet to its knees in 2016 provided a clear indicator of the precarious state of IoT security.
The root of such weaknesses lies essentially within the security architecture of the IoT itself.
IoT architecture relies upon a distributed client-server model which uses a central authority to manage both the IoT devices as well as the data generated across an IoT network.
For IoT data to be trusted, all trust requests are aggregated into a single location which creates a sole point of security intelligence that can compromise IoT security. This is how Mirai-style botnet attacks can succeed.
Basically, during such an attack, IoT devices are unable to adapt their behaviour because they are not considered “smart” enough to make security decisions without the help of the central authority.
In an interview with computerweekly.com Joseph Pindar, Director for Strategy in the CTO office at Gemalto, and co-founder of the Trusted IoT Alliance, a non-profit group that advocates the use of blockchain to secure IoT ecosystem outlined why he believes Blockchain could hold the answer to true IoT security.
Pindar explained how blockchain removes the single point of decision-making that leads to failure, by enabling device networks to protect themselves in other ways, such as allowing devices to form group consensus about what is normal within a given network, and to quarantine any nodes that behave unusually.
Blockchain can play a crucial role in building trust in IoT dataIn addition to this blockchain can play a crucial role in building trust in IoT data by enabling what Pindar called the five digital security primitives: availability, auditability, accountability, integrity and confidentiality.
In blockchain, data is automatically stored in many locations and is always accessible to users.
For auditability and accountability, a private, permission-based blockchain is used – where all users are authorized to access the network – and because all data stored on the blockchain is signed, each device is accountable for its actions.
With regards to integrity, blockchain is as we’ve outlined above a public ledger of data entries.
With every entry, deletion or correction of data being confirmed across the network across a fully verifiable complete chain of events.
Further to this, there is also another perhaps less obvious but equally important benefit of utilizing Blockchain within IoT systems which Pinder raises.
There is a fairly widespread mindset amongst IT executive management regarding securing the industrial Internet which is that once a sensor, device or controller has been deployed and is working, it cannot be touched.
“Even if there is a known security vulnerability, it is not worth fixing it, because there is a chance that the security patch would cause problems elsewhere in the system that no one knows how to fix,” explained Pindar when speaking to Computer Weekly’s Aaron Tan “But as cloud computing has demonstrated, there are continual failures of devices and systems when operating at very large scale.”
“Simply put, it is not possible to manage large-scale systems that are fragile and not resilient to failure – as is the case with many current industrial IoT and OT systems.”
And the solution to this which Pindar recommends is to allow continuous deployment of software updates, alongside blockchain technology after devices have been deployed, with little or no downtime through an over-the-air update system - something he believes delivers both cost and operational efficiency when delivering over-the-air updates and patching to IoT devices and sensors.
With the IoT becoming more and more prevalent amongst field service organizations, the suggestions Pindar makes regarding the application of Blockchain in such systems should indeed be an important consideration for field service organisations as they establish their IoT processes.
The final piece of the 3D printing puzzle?
However, there could be yet another important place for blockchain within the field service sector, it could just be the missing piece of the puzzle in resolving one of the biggest challenges within our sector, namely managing the spare parts supply chain.
3D printing has for a long time been touted as a potential solution to getting parts needed to engineers as soon as possible, but one potential hurdle has always been how organisations control the licensing of the spare parts to ensure that firstly if the customer has 3D printing capability on-site - which has been one suggested use case, how can the provider ensure they don’t simply print off as many parts as needed once they have initially received the schematics file.
Similarly, by sending the parts data across in a digital file, the potential for such a file to make its way into the hands of unscrupulous third parties happy to make unauthorized parts for sale elsewhere is also a cause for concern for many organizations. Frankly, the risk to their IP and the significant loss of revenue this could lead has meant that many OEMs still view 3D printing with a distinct lack of trust.
However, could Blockchain perhaps hold the solution to such fears?
This certainly seems to be the thinking behind one Italian startup called 3D-TOKEN, which aims to integrate Blockchain and 3D printing technologies, in order to create a “unique, decentralized, global Just-In-Time Factory 4.0 for this century’s digital revolution.”
If successful it could certainly set a precedent for how Blockchain and 3D printing could work in harmonyAside from cramming as many manufacturing buzz phrases into their mission statement as possible, it seems it is certainly a concept that could have a potentially huge impact on service organizations within OEMs.
The goal for 3DToken is to connect thousands of 3D printers in a network hub based in Blockchain. In short, the plan is to create a Blockchain-managed network hub of desktop 3D printers.
The project will be used to bring just-in-time small-to-medium scale digital manufacturing to a new level.
Coin Telegraph described the startup as being capable of “accelerating the 3D printing market to its full potential” by changing up industry norms on product cost and time to market.
Whilst this project is still very much in its infancy, they have made impressive progress to date and although the focus on desktop 3D printers would suggest a consumer-centric approach initially as opposed to something suited for industry, if successful it could certainly set a precedent for how Blockchain and 3D printing could work in harmony, and the concept should at the very least give many OEMs food for thought as to how they could harness the potential of 3D printing. Especially as a means of bypassing much of the often highly complex service supply chain.
Be social and share
Mar 29, 2018 • Features • Augmented Reality • Daniele Pe • Future of FIeld Service • Virtual Reality • Delta Partners • Gunish Chawla • Irish Monipis • technology
Gunish Chawla and Daniele Pe, Senior Principals and Irish Manipis, Senior Business Analyst at Delta Partners have published a deep and far-reaching exploration of exactly how Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality are set to become key platforms in...
Gunish Chawla and Daniele Pe, Senior Principals and Irish Manipis, Senior Business Analyst at Delta Partners have published a deep and far-reaching exploration of exactly how Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality are set to become key platforms in the future.
We are already seeing an increasing number of forward-thinking field service organisations adopting such platforms so this detailed report provides some excellent, well-resourced context about the future of a technology set to play a very big part in the future of field service management...
The relevance of AR and VR in re-shaping user experiences and the implications on the telecom industry.
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) have the potential to become the next big platforms after PC, web, and mobile. Isolated applications of AR and VR have been around for a while, but the technologies to unlock their potential have only recently become available. We expect AR and VR to fundamentally transform how consumers interact in the physical world and how enterprises run their operations.
Augmented and Virtual Reality: Distinct but complementary technologies
In a nutshell, AR overlays digital imagery onto the real world, while VR immerses a user in an imagined or replicated world (see figure 1 below).
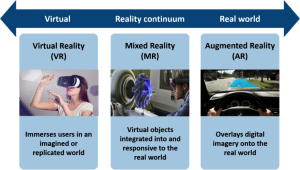 Figure 1: AR and VR overview
Figure 1: AR and VR overviewFundamentally, AR and VR create a new way of interaction using gestures and graphics that are highly intuitive to humans. VR creates an illusory “sense of presence” in an imaginary world created through a computer-generated simulation. For instance, this allows users to experience travelling, shopping, creating, talking or interacting with people remotely in a completely different way. In contrast, AR allows people to access digital information in their real-world environments, thereby allowing “simultaneous existence” in both physical and digital worlds. Both AR and VR are transformative in nature and likely to co-exist as immersive platforms.
A whole new realm of opportunities
We are still at the beginning of the AR and VR revolution, but there is no doubt that they have the potential to revolutionise multiple industries over the next five to ten years, transforming the way we interact with the surrounding world, unlocking new experiences, increasing productivity and efficiency (see figure 2.)
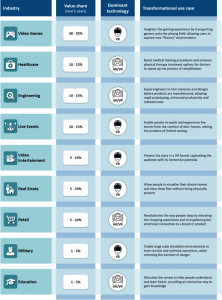 Figure 2: Selected AR and VR transformational use cases
Figure 2: Selected AR and VR transformational use casesFrom the use cases, one can infer that AR and VR will create a shift that is comparable, if not greater, than that of the smartphone and underlying platforms.
This potential has been recognised by major technology giants and OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturer).
Facebook made an early bet in 2014 when it acquired Oculus for $2.1bn and since then it has acquired over ten other AR/VR players. Other technology giants have followed suitFacebook made an early bet in 2014 when it acquired Oculus for $2.1bn and since then it has acquired over ten other AR/VR players. Other technology giants have followed suit – Google launched Google Cardboard, Google Glass and backed Magic Leap; Microsoft launched HoloLens and Apple acquired AR software maker Metaio. Samsung has multiple projects coming from its in-house C-lab incubator such as Monitorless (PC-viewing glasses), Vuildus (VR home furnishing), Relúmῐno (smart aid for the visually impaired) and TraVRer (360-degree travel video platform).
While technology giants and OEMs have been leading the charge, telecom operators have been slow to react, but, in recent years, we see operators in developed markets beginning to dip their toes in the water. For example, Telefonica launched start-up incubator Wayra currently supporting eight VR and four AR start-ups. SK telecom has developed 360-degree VR live broadcasting capabilities and BT is trying to revolutionise the sports experience through VR enabled football match telecast.
For AR and VR to become the next big platforms, challenges must be overcome
While significant progress has been made in this space over the past few years and the ecosystem today has hundreds of companies, thousands of employees and over $4.5 billion invested, with expectations to become an $80-100 billion industry by 2025, AR and VR today are still emerging technologies.
For AR and VR to fully materialise and provide the impact described above, significant hurdles need to be overcome.
These can be grouped into four main categories:
- Bulky and expensive devices: Despite the emergence of lower cost hardware options such as Google Cardboard ($15) and Google Daydream ($99), the majority of AR and VR equipment is very costly, e.g. HTC Vibe ($799), Oculus Rift ($600) and Google Glass ($1,500). In addition to the hefty price tags, the current AR and VR equipment is bulky and cumbersome (e.g. presence of wires). Though it may be suitable for static experiences (e.g. watching a movie), it will be a challenge in an immersive environment that requires freedom of movement and authenticity as functionality (e.g. employees in the manufacturing industry, who deal with dangerous machinery, and cannot be exposed to potential hazards).
- Scarcity of “killer” content and applications: Without a wide variety of popular applications, it will be hard for AR and VR to reach mainstream success. Although there are many applications on the gaming and video front, AR and VR have yet to find their “superstar app” – i.e. the use case that makes the technology fundamental for both consumers and enterprises.
- Limited penetration of technically ready smartphones and devices: Technical issues such as smartphone battery life and graphical capabilities hinder the adoption of AR and VR. To have the best AR and VR experience, devices need to have superior image display and audio capabilities (at least 2560x1440 resolutions), powerful processors (e.g. 820 Snapdragon), large memory space and adequate battery life. Today less than 10% of 2.8+ billion smartphones worldwide are compatible with Samsung Gear and Google Daydream.
- Insufficient network speed and latency: Fully immersive 360-degree experiences require at least 25Mbit/s for streaming and can go up to 80-100Mbit/s for HD TV. With a global average of 7.2 Mbit/s, only about 12% of global connections satisfy these requirements. In addition, low latency is critical to delivering the best AR and VR experience because even small delays can have a disorientating effect. For instance, when a user turns and the landscape does not move simultaneously, the user may experience motion sickness. VR requires less than 1ms latency and currently, the global average latency is 36ms on fixed and 81ms on mobile.
The case of Pokémon Go (free-to-play, location-based AR game) clearly illustrates the situation. When Pokémon Go was released in July 2016, it exceeded 100m downloads within a month of its release, becoming the most downloaded mobile gaming app of 2016. It single-handedly proved how profitable and widespread AR could be, generating over a billion dollars in revenue for developer Niantic.
This was achieved with a game that was “simple” enough to work with smartphones without the need of any additional device and the content was a “killer hit” as demonstrated by the take-up. Despite the success, key issues emerged in terms of device capabilities and network. Pokémon Go requires the smartphone device to have long battery life, GPS sensor and compass.
Users without these functionalities would drain their batteries within a few hours or have to settle for a pared down version of the game which detracted from their enjoyment and experience. On top of device capability issues, Pokémon Go also experienced issues on mobile networks. Despite only taking up roughly 0.1% of the overall traffic, the game accounted for >1% of all sessions on the network.
This ten times differential was the result of communication sessions opening with Niantic servers every time an event happened in the game. Driven by the massive uptake, the cumulative effect from both bandwidth and sessions negatively impacted networks, especially when the game drove large groups of players towards specific geographical areas.
What role can telecom operators play in the AR and VR ecosystem?
As mentioned, telecom operators are yet to make a credible play in this space. However, we believe that they can play a fundamental role in helping overcome some of the challenges illustrated and thereby enable earlier materialisation of the AR and VR promise. This is where operators’ typical strengths such as network infrastructure deployment or devices distribution capabilities come into play. But beyond helping drive these new technologies, we believe AR and VR have the power to transform the role of operators in the ecosystem.
If we believe that AR and VR will be the next big platforms, we should be able to imagine a world where we no longer look at our phones, but rather look up to visualise the content in front of our eyesIf we believe that AR and VR will be the next big platforms, we should be able to imagine a world where we no longer look at our phones, but rather look up to visualise the content in front of our eyes, and interact with the device through machine-learning enabled voice or visual recognition. In this scenario, the role of the smartphone would be significantly diminished.
This would provide a fresh opportunity for operators. Operators have missed the opportunity to play a significant role in the smartphone ecosystem - in terms of capturing a share of a customer’s mind and interaction time, and therefore monetising it. However, if the role of the smartphone diminishes, and new platforms take over, then opportunities arise for operators to play a pivotal role in the digital ecosystem beyond connectivity. This is where the roles of ‘open enablement platform’ and ‘application and content provider’ become relevant for operators.
Pragmatically, we have categorised the role of operators in the AR / VR ecosystem in four groups based on the level of involvement of the operator and the expected transformational results: 1) Device distributor, 2) Connectivity provider, 3) Open enablement platform, and 4) Application and content provider.
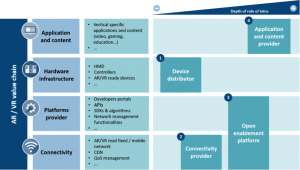 Figure 3: Telecom operators’ role in the AR and VR ecosystem
Figure 3: Telecom operators’ role in the AR and VR ecosystem- As a ‘Device distributor’, operators would resell devices to end-users, and make them more accessible by subsidising, leasing or financing them as operators have been doing for smartphones.
- As a ‘Connectivity provider’, operators would need to ensure that last mile networks have intelligent traffic management solutions, high quality compression algorithms, low-latency and high bandwidth capabilities to offer users immersive experiences that are realistic, engaging and entertaining. As such, 5G technology will be critical in helping overcome network limitations. Similarly, the Telecom Infra Project (TIP), an initiative launched by Facebook in collaboration with operators, infrastructure providers and system integrators, focused on tackling the engineering challenges of delivering high-resolution video and virtual reality, will play a key role in enabling AR and VR take-up. However, driving these network transformation projects will require large investments on top of ongoing CAPEX requirements. Operators need to determine whether they can successfully and sustainably monetise this investment, which poses the following key questions:
- Will the surge in data usage from AR and VR applications be enough to justify the effort? Could operators monetise the quality of service demanded by AR and VR through specific tariffs or network boost add-ons?
- Can an AR and VR ready network be leveraged as a tool to boost differentiation, hence customer acquisition and retention, therefore driving the operators’ revenue share in the market?
- In an ‘Open enablement platform’ role, operators position themselves as the ‘glue’ that brings together different players in the AR/VR ecosystem: end-users, developers, devices manufacturers and content creators, effectively allowing different players within the ecosystem to develop solutions, ensuring interoperability and widespread adoption. This enablement platform will not only have typical network functionalities such as QoS management (deploying bandwidth intelligently based on pre-defined rules and parameters), robust content delivery network, and compression algorithms (to reduce network strain), but also a developer portal with tools such as APIs (to connect the different ecosystem providers and enable the longer tail of developers), dedicated SDKs, ready-to-use ‘basic’ AR/VR algorithms, billing capabilities and an analytics layer.
- As an ‘Application and content provider’, operators would collaborate with industry players to deliver AR and VR specific applications and content (e.g. video, gaming, shopping, manufacturing, etc.), where AR and VR will support specific use cases. This will help operators explore new revenue streams directly through app/content-based revenue models, and revenue sharing with app/content developers but also indirectly through improved positioning (meaning better customer acquisition and retention), and higher customer engagement (translating in a share of wallet and data usage boost). Korea Telecom (KT) is an example of an operator that is going down this path. For the 2018 PyeongChang Winter Olympic Games, KT plans to release a whole suite of AR and VR applications. These include Sync View (viewers watch the games through athlete’s lens), Interactive Time Slice (100 camera angles and screens), 360 VR Live (panoramic view of the games) and Omni Point View (all around view of the games). Along similar lines, BT is planning to drive its ambition to revolutionise sports watching to a new level by delivering fully-immersive, interactive VR content, which will place people right at the heart of the action.
In summary
While AR and VR are still emerging technologies, their mainstream adoption will increase dramatically as hardware costs fall, device functionality gets more sophisticated, more ‘killer’ content is developed, and network speed and latency improve. While it’s true that in the short-term, AR and VR will remain relatively niche, the mid to long-term potential could be transformational.
Operators can adopt a passive approach, where no specific step is taken in the advancement of the AR and VR industry beyond the ongoing modernisation of the network (e.g. 5G deployment), which naturally supports the materialisation of the AR and VR promise. This is unlikely to result in significant monetisation potential, and could further decrease operator relevance in the ecosystem, pushing operators further towards being pure connectivity providers.
Digitally-minded ambitious operators can champion and drive the AR/VR space by positioning themselves deeper in the value chain as a ‘platform enabler’ and/or ‘application and content provider’ Alternatively, digitally-minded ambitious operators can champion and drive the AR/VR space by positioning themselves deeper in the value chain as a ‘platform enabler’ and/or ‘application and content provider’. This implies early investment in the required network capabilities, a build-up of additional competencies on top of the connectivity layer and collaboration with technology players that are pushing the boundaries of the industry to develop end-user solutions. Operators that choose this path and do it right can leverage the novelty factor to reposition themselves within the ecosystem of tech and device players and in the eyes of the end user.
The telecom industry track record suggests this is a long shot for operators. Over the last decade, they have generally been poor at innovation and have time and again missed the opportunity to leverage their unique assets to position themselves strongly in the digital space. Nevertheless, there is intention from many leading operators to make a serious play within the digital space – AR and VR could well be the foundation to spearhead this transformation.
Be social and share
Mar 27, 2018 • News • Future of FIeld Service • MWC 2018 • Ericsson • IoT • IoT Accelerator Marketplace • Jeff Travers
Ericsson is launching the IoT Accelerator Marketplace to help address the need for collaboration within the digital ecosystem community and benefit developers and service providers alike.
Ericsson is launching the IoT Accelerator Marketplace to help address the need for collaboration within the digital ecosystem community and benefit developers and service providers alike.
For service providers, it is a catalogue to find IoT apps from the global ecosystem to offer enterprise customers and provides a shorter time to market for new offerings to their enterprise customers.
For application developers and application partners, it is a window to an IoT ecosystem to connect with service providers through one single platform, exposing global cellular connectivity APIs. It also includes monetization and settlement capabilities to facilitate monetization and billing across the ecosystem.
The launch of IoT Accelerator Marketplace will unlock the potential for different players in the value chain to deliver value. It is another stepping stone to make 5G a reality by enabling massive adoption of massive IoTCarrie MacGillivray, Group Vice President, Internet of Things & Mobility at Market Intelligence firm IDC, says: “Communications service providers are racing to scale and differentiate in the fast-moving IoT market. It’s necessary for these service providers to have a robust developer ecosystem that helps them compete. For developers working across multiple service provider networks and platforms, the challenges of fragmentation are addressed by utilizing APIs that apply globally and are consistent across all mobile networks.”
Jeff Travers, Head of IoT, Ericsson, says: “The launch of IoT Accelerator Marketplace will unlock the potential for different players in the value chain to deliver value. It is another stepping stone to make 5G a reality by enabling massive adoption of massive IoT. This supports service providers as they seek to expose network connectivity IoT APIs and monetize these assets.”
Application developers can benefit from a new go-to-market exposing their offering globally through Ericsson. This will enable app developers to scale their business and at the same time develop applications based on cellular connectivity APIs with added value for enterprises, such as fast and automated device and subscription onboarding, higher security, ubiquitous cellular coverage around the world improved for indoor utilization, and superior handling of battery life.
Service providers and application developers can request access to the IoT Accelerator Marketplace here: IoT Accelerator Marketplace
IoT Accelerator Marketplace is being demonstrated by Ericsson at MWC 2018. Ericsson’s IoT Accelerator is a cloud-based horizontal offering comprising of platform services and professional services, for service providers. It provides continuous incremental functionality offered as a Service to enable agile creation and deployment of solutions for the Internet of Things.
Be social and share
Mar 26, 2018 • News • Future of FIeld Service
Jacobs Engineering Group and Atos, a global leader in digital transformation, have reached a non-exclusive collaboration agreement to provide predictive, condition-based maintenance and field services optimization solutions to clients across...
Jacobs Engineering Group and Atos, a global leader in digital transformation, have reached a non-exclusive collaboration agreement to provide predictive, condition-based maintenance and field services optimization solutions to clients across industry sectors including water, energy, transport, aviation, nuclear and the built environment.
The enhanced data capture and analysis offers clients greater understanding of their assets, helping them to reduce operational and reactive maintenance costs, optimize performance, and increase return on asset investment.
“This collaboration with Atos will help us create more opportunities to leverage disruptive technology and deliver strategic digital innovation for complex government, infrastructure and industrial programs,” explained Jacobs Buildings and Infrastructure Europe Senior Vice President and General Manager Donald Morrison. “With our in-depth industry knowledge and combined digital capabilities, we are well positioned to help our clients achieve performance excellence and maximize their opportunities in this dynamic technology space.”
The digitization of front-line operations means solutions that reduce cost through predictive and preventative maintenance are in high demand“All industries are undergoing huge transformation due to the maturing of the Internet of Things (IoT) and analytics services,” said Paul Albada Jelgersma, Senior Vice President, Global Head of Atos IoT Services. “The digitization of front-line operations means solutions that reduce cost through predictive and preventative maintenance are in high demand. This is a highly synergistic collaboration and our recognized expertise in end-to-end strategy covering consulting, development, advanced analytics, managed IoT and IoT security will enable us to provide integrated solutions to clients from the outset.”
Harnessing the professional technical services expertise of Jacobs with the digital and IoT capabilities of Atos, the combined offering will provide further value to clients through real-time insights that detect anomalies and performance patterns, determine critical assets and understand the root cause of asset failure. This enables clients to better anticipate potential asset failure and performance issues and to proactively plan for timely maintenance and replacement.
The collaboration will leverage part of the Atos Codex portfolio of offerings, together with Jacobs Connected Enterprise (JCE), a suite of integrated digital capabilities and solutions in data analytics, IoT deployment and cybersecurity.
The agreement will initially focus on the U.K. with the option to extend to other markets.
Be social and share
Mar 16, 2018 • video • Features • Future of FIeld Service • Kieran Notter • Millenialls • research • GE Digital • IoT • servicemax
Kris Oldland, Editor-in-Chief, Field Service News and Kieran Notter, Director, Global Customer Transformation, ServiceMax from GE Digital explore the findings of an exclusive independent research conducted by Field Service News and sponsored by...
Kris Oldland, Editor-in-Chief, Field Service News and Kieran Notter, Director, Global Customer Transformation, ServiceMax from GE Digital explore the findings of an exclusive independent research conducted by Field Service News and sponsored by ServiceMAx from GE Digital.
In this second excerpt from the full one-hour long webcast, Oldland and Notter discuss both what the must-have skills of the field service engineer are likely to be in the not too distant future taking into account the impact of industry mega-trends such as servitization, digitalisation and an incoming army of millennials.
Want to know more? The full webcast PLUS an exclusive report based on the findings of this research is available for Field Service News subscribers.
If you are a field service practitioner you may qualify for a complimentary 'industry practitioner' subscription. Click here to apply now!
Be social and share
Mar 13, 2018 • video • Features • Future of FIeld Service • Preventative Maintenance • Dan Sewell • Espresso Servic • IoT • Asolvi
Kris Oldland, Editor-in-Chief, Field Service News talks exclusively to Dan Sewell, COO of Espresso Service about preventative maintenance.
Kris Oldland, Editor-in-Chief, Field Service News talks exclusively to Dan Sewell, COO of Espresso Service about preventative maintenance.
Dan and the team at Espresso Service have embraced the Internet of Things and preventative maintenance with open arms and have already seen some fantastic benefits from doing so.
We look at what those benefits and improvements were as well as getting Dan's advice for any organisation looking to follow in their footsteps exploring what the best initial steps are for adopting such an approach.
This video series is sponsored by:
Be social and share
Mar 07, 2018 • Features • Future of FIeld Service • future of field service • Jan Van Veen • Michael Blumber • moreMomentum • Bill Pollock • Blumberg Associates • Strategies for Growth
In the Big Discussion, we will take one topic, bring together three leading experts on that topic and put three key questions to them to help us better understand its potential impact on the field service sector...
In the Big Discussion, we will take one topic, bring together three leading experts on that topic and put three key questions to them to help us better understand its potential impact on the field service sector...
This issue our topic is the what to expect in 2018 and our experts are Michael Blumberg, Blumberg Advisory, Bill Pollock, Strategies for GrowthSM and Jan Van Veen, moreMomentum
So let's tackle the first question...
What is the biggest challenge facing field service companies in the next 12 months?
 Bill Pollock: The biggest challenge facing field service companies in the next 12 months will be keeping up with customer expectations for service delivery as they continually raise the bar with respect to performance. This is not necessarily a “new” challenge – it actually has been one of the main challenges for field service companies year-after-year. However, the current environment of constantly improving technology and its availability through both the traditional, “tried-and-true” FSM solution providers plus the introduction of several new technology-based solution vendors makes this challenge particularly daunting for many field service managers.
Bill Pollock: The biggest challenge facing field service companies in the next 12 months will be keeping up with customer expectations for service delivery as they continually raise the bar with respect to performance. This is not necessarily a “new” challenge – it actually has been one of the main challenges for field service companies year-after-year. However, the current environment of constantly improving technology and its availability through both the traditional, “tried-and-true” FSM solution providers plus the introduction of several new technology-based solution vendors makes this challenge particularly daunting for many field service managers.
Selecting which technology to implement is not the only challenge, however; field service companies must also be able to choose the right solution vendor to help them design, implement and support their newly acquired technology. Some of the most challenging questions may be, “If we’re already using Microsoft Dynamics 365 for our CRM solution, should we also use Microsoft Field Service?”; similarly, “If we’re already using Salesforce for our sales and marketing management, should we also use their Field Service Lightning solution?” Other questions may include, “Should we use one of the traditional FSM solution providers, such as Astea, ClickSoftware, IFS/Metrix, ServicePower, etc., or one of the newer providers?”; or “Should we use a UK-based solution provider, such as Fast Lean Smart, or Kirona, etc., rather than an off-shore-based provider?”
The choices are many – and no less challenging than they have been in the past!

Jan Van Veen: Most manufacturing companies and their service units struggle to innovate and change quick enough.
Technology is developing at an increasing pace; adoption of new technology has never been so rapid. In the digital era, we can expect competition from new entrants like innovative data- and algorithm-driven businesses.
So, the name of the game now is ‘Adapt and Thrive’ (or ‘Stagnate and Die’). The winners of the next decades will be those who can maintain a high speed of business innovation and change, and can cope with a high level of uncertainty and unpredictability.
What is holding most manufacturing companies back is;
- Slow change, whether it’s small change or bigger change
- Stuck in business-as-usual: innovations are predominantly incremental improvements of the status quo
- Lack of influence: individuals at all levels and in various departments see the threats, opportunities and the lack of progress, which frustrates them
I believe that one of the biggest challenges right now is to increase momentum for rapid and fluent change from the inside, and empowering employees at all levels to take ownership.

Michael Blumberg: In the short term, field service companies must also find ways to balance service quality and productivity with their financial goals and objectives (think costs and profits), all while striving to maintain exceptional levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty.
This objective holds true for any 12-month period under consideration whether the year is 2018, 2008, or 2028.
The challenge lies in developing and implementing a winning strategy based on current financial and operating constraints that each company faces.
Be social and share
Mar 06, 2018 • News • AI • Artificial intelligence • Future of FIeld Service • Oskar Klingberg • Wiraya • Wiraya Solutions • EU • European mobile telecom operators • Customer Satisfaction and Expectations
Wiraya, a Marketing Technology firm based in Sweden which develops a Managed Mobile Customer Activation software, has been awarded €2 million in innovation grants by the European Commission, for the development of Wiraya Activation Intelligence...
Wiraya, a Marketing Technology firm based in Sweden which develops a Managed Mobile Customer Activation software, has been awarded €2 million in innovation grants by the European Commission, for the development of Wiraya Activation Intelligence (“Wiraya AI”).
The contribution is intended to enable further development, validation and optimisation of Wiraya’s artificial intelligence software to help Europe’s mobile operators improve customer value for their subscribers, and thereby customer loyalty.
The new functionality, Wiraya AI, automatically creates interactive voice and text communications, which allows individual dialogue with large customer groups. With such deployments of AI being predicted to potentially revolutionise the customer experience across a range of use cases including support issues, this development could be an interesting development for field service organisations.
We are really proud to be one of the few companies selected by the European Commission. The grant gives us a great opportunity to be able to drive the development of artificial intelligence within customer communication in Europe - Oskar Klingberg, CEO, Wiraya SolutionsCurrently, European mobile telecom operators are facing continuing rising industry challenges to tackle low customer satisfaction and loyalty and despite advanced churn prediction models, operators still often communicate with their customers as if they were still prospects, using generic communication that erodes trust and commitment. This is a challenge that Wiraya are aiming to tackle.
Using machine learning, the software predicts and customises what, when and how to communicate with each individual, by matching the individual’s profile with specific communication journeys. With the implementation of Wiraya AI, 5% of the annual churning customers can be saved each year, corresponding to substantial savings for the operator, and increased customer satisfaction.
“We are really proud to be one of the few companies selected by the European Commission. The grant gives us a great opportunity to be able to drive the development of artificial intelligence within customer communication in Europe. We have always tried to challenge ourselves by identifying and solving important industry-specific business problems. For the telecom sector, AI functionality will solve resource-intensive and complex customer communication flows with highly effective, automated personal dialogues.” says v, CEO of Wiraya Solutions.
The development of AI functionality begins with pilot projects in 2018 and then full commercial launch in 2019. Initial tests suggest up to 5 times higher conversion rates compared with today’s way of communicating, while delivering substantial yearly savings.
Klingberg adds: “We are now developing the functionality specifically for mobile operators, but our plan is to implement the functionality across other industries, proving the same opportunity for a whole range of businesses.”
Should the pilots be successful it will be interesting to see if this could as act as a proof of concept to roll out across over service-centric sectors.
Be social and share
Mar 06, 2018 • video • Features • AGeing Workforce • AR • Artificial intelligence • Future of FIeld Service • Kieran Notter • research • Research • drones • IoT • servicemax
Kris Oldland, Editor-in-Chief, Field Service News and Kieran Notter, Director, Global Customer Transformation, ServiceMax from GE Digital explore the findings of an exclusive independent research conducted by Field Service News and sponsored by...
Kris Oldland, Editor-in-Chief, Field Service News and Kieran Notter, Director, Global Customer Transformation, ServiceMax from GE Digital explore the findings of an exclusive independent research conducted by Field Service News and sponsored by ServiceMax from GE Digital.
In this excerpt from the full one-hour long webcast, Oldland and Notter discuss both the challenges and opportunities of an ageing workforce within the field service sector and assess whether there is any substance to fears that we are facing an ageing workforce crisis.
Want to know more? The full webcast PLUS an exclusive report based on the findings of this research is available for Field Service News subscribers.
If you are a field service practitioner you may qualify for a complimentary 'industry practitioner' subscription. Click here to apply now!
Be social and share


















 Field Service News is published by 1927 Media Ltd, an independent publisher whose sole focus is on the field service sector. As such our entire resources are focused on helping drive the field service sector forwards and aiming to best serve our industry through honest, incisive and innovative media coverage of the global field service sector.
Field Service News is published by 1927 Media Ltd, an independent publisher whose sole focus is on the field service sector. As such our entire resources are focused on helping drive the field service sector forwards and aiming to best serve our industry through honest, incisive and innovative media coverage of the global field service sector.
Leave a Reply