Study from SCALA reveals third-party logistic companies (3PLs) are falling behind in innovation and productivity.
ARCHIVE FOR THE ‘management-2’ CATEGORY
Aug 14, 2019 • News • management • report • Parts Pricing and Logistics
Study from SCALA reveals third-party logistic companies (3PLs) are falling behind in innovation and productivity.
SCALA surveyed a selection of the UK’s best-known businesses and 3PLs (whose revenue runs into the billions and whose number of clients run into the thousands) to ascertain companies’ satisfaction rates and areas of concern regarding the performance of their 3PLs.
Aug 14, 2019 • Managemenet • management • return on investment • field service management • field service software • Technology Investment • Building a case for investment • HSO
In this series, which features a number of features based around an exclusive white paper published by Field Service News in partnership with HSO we are looking at three core arguments service directors when trying to secure investment from their...
In this series, which features a number of features based around an exclusive white paper published by Field Service News in partnership with HSO we are looking at three core arguments service directors when trying to secure investment from their board in new field service management systems. Having taken a look at two of the more traditional arguments so far in Return on Investment and Health and Safety we now turn our attention to a newer facet of the argument, can your organisation afford not to invest if it means you are going to be at a competitive disadvantage...
Aug 13, 2019 • News • management • PTC • first time fix • Service Execution Management
Is investing in service execution solutions enough to improve first-time fix rates and achieve high levels of equipment uptime? Chris Mitchell from PTC explains more...
Is investing in service execution solutions enough to improve first-time fix rates and achieve high levels of equipment uptime? Chris Mitchell from PTC explains more...
Improved asset uptime, first time fix rates, repeat visit avoidance; all are undoubtedly some of today’s OEM’s most relevant metrics and challenges: revenues from service offerings, whether it be PBL contracts or more traditional service models, are too significant to be ignored.
Not least through industrial applications of the IoT we see an abundance of applications and use cases relating to operating and servicing equipment, whether in the field or in the factory. The way we can now easily connect to assets and operate, monitor and diagnose them remotely is simply fantastic.
Many also focus on applications of augmented reality to not only improve the way equipment is maintained in established markets, but also how it can be maintained in emerging markets, where experience and training is simply lacking.
The trap many OEMs fall into, however, is the notion that investing into the improvement of such service execution challenges is sufficient.
Improving asset uptime in this way has certainly never been easier to accomplish - all the enabling technology is here today! Adopting these new technologies to improve the service experience are essential. However, there is a huge aspect to servicing assets, which is still widely ignored: Spare parts inventories are not optimised – so the right part is too often not available at the right time, place and cost: Companies’ investment in their spare parts inventories are simply too high.
Balance sheets are laden with huge amounts of cash that are tied up in incorrect inventories and need to be freed up to be spent in other areas of the business or to simply improve operating margins. Bills for expediting shipments and cannibalising production inventory are largely too high.
The challenge is that unlike production inventory planning, spare parts demand, and therefore inventory, is much more difficult to predict. Too often historical demand is used to forecast but, in most cases with low levels of accuracy.
Not often enough is spare part demand forecasted by employing causal factors, where forecasts are calculated based on your equipment usage rates and average values for casuals, such as meantime between failure rates. OEMs would now able to use real-time usage data and predicted failures of the asset to further improve forecasts and therefore optimising parts availability further.
"Too often historical demand is used to forecast but, in most cases with low levels of accuracy..."
Regrettably the required information is often not provided by other parts of the organisation, the negative consequences of which are not addressed in the organisation. Levels of equipment uptime and part availability are far lower than they should be. Brand loyalty suffers, customers buy parts (and equipment) elsewhere and revenues are impacted.
So how do we solve the conundrum of keeping inventories low whilst exceeding customer expectations in terms of equipment uptime and part availability?
The approach needs to be all encompassing if you really want to offer first class service to your customers at the lowest possible cost and should incorporate the following:
1. Improve parts availability by improving forecasting, inventory optimisation and supply planning - this will drive immense value within a few months of implementing and will drastically reduce inventories, equipment downtime and improve first time fix rates. You now have a parts supply chain, which perfectly supports an optimised service and repair network.
2. Automate field service operations by ways of a connected optimisation solution wherever possible, by leveraging exception monitoring and failure prediction from connected assets - let the asset tell you it’s failing rather than the customer when it’s too late - this will further reduce downtime and speed up repair time frames.
3. Enable the field technician (or customer) in the most effective way, by leveraging digital service content delivery through phones, tablets or VR, AR or MR headsets, leveraging augmented and virtual reality technologies. This will speed up repair or maintenance steps and ensures technicians operate effectively and based on the most up to date information available, information that is delivered from downstream CAD and PLM solutions.
4. Ensure service contracts and parts are priced correctly. This way you ensure sales are profitable and customers return to you time and time again for repeat business. This is also the ultimate way to combat the threat from copy pars.
There are many more applications of the above technologies, not least training and enablement, but hopefully it becomes clear that implementing one technology without the other will only unlock some of the value.
So in summary: the key to an optimised field service operation is not just the use of best of breed execution tools such as AR, Field Service Management and Service Parts information. The technician visit can only be successful first time if the correct spare part is made available, i.e. if the demand for the spare part has been predicted as accurately as possible and has been made available to the technician!
Chris Mitchell is Director Business Transformation - Servigistics Business Unit at PTC.
Jul 30, 2019 • health and safety • Managemenet • management • field service management • field service software • Technology Investment • Building a case for investment • HSO • Business Development
In this series, which is based around an exclusive white paper published by Field Service News in partnership with HSO, we are exploring three core arguments service directors can make to the board to secure investment in implementing or upgrading...
In this series, which is based around an exclusive white paper published by Field Service News in partnership with HSO, we are exploring three core arguments service directors can make to the board to secure investment in implementing or upgrading their field service management systems. In the second part of the series we look at how you can build a case based around health and safety...
Jul 23, 2019 • Managemenet • management • return on investment • field service management • field service software • Technology Investment • Building a case for investment • HSO
In a new series based around an exclusive white paper published by Field Service News in partnership with HSO we look at three core arguments service directors can make to the board to secure investment in implementing or upgrading their field...
In a new series based around an exclusive white paper published by Field Service News in partnership with HSO we look at three core arguments service directors can make to the board to secure investment in implementing or upgrading their field service management systems. In the first part of this series we look at how you can build a case based around return on investment...
Jun 06, 2019 • News • management • Survey • Customer Satisfaction and Expectations
Businesses are out of touch with their customers and overestimate the quality of the customer service they provide, according to new research from Pegasystems Inc. the software company empowering digital transformation at the world’s leading enterprises.
Research firm Savanta surveyed 12,500 global customers, businesses executives, and customer-facing employees for a one-of-a-kind, three-dimensional perspective on the state of customer service today. The research identified key customer service frustrations and revealed that many businesses don’t know their customers well enough to provide the level of service their customers want.
It also found that many organizations aren’t fully committed to providing the level of service they aspire to and run the risk of losing customers to competitors as a result. The good news? Customers, employees, and business leaders all agree on what matters most, so a clear roadmap exists.
Key findings of the study include:
• Business decision makers are out of touch:
Four times the percentage business leaders (40 percent) as customers (10 percent) rate the current standard of customer service as ‘excellent,’ while only 23 percent of customer-facing staff rate their organization’s service the same way. Similarly, an overwhelming 89 percent of decision makers and 73 percent of employees feel their organization provides an overall positive level of customer service, but only 54 percent of customers feel the same way. In addition, 71 percent of business leaders think they provide better customer service than their competitors – a number that is mathematically impossible to achieve.
• Are businesses really committed to providing good customer service?
While 81 percent of business decision makers consider customer service as either their main or key competitive differentiator, 33 percent of customer-facing employees say they face no consequences for providing bad customer service. Meanwhile, 48 percent of customer-facing employees say they face barriers to providing good service.
• Poor service is driving customers mad:
88 percent of customer-facing employees say that customer service is a priority within their business, but the customers tell a different story. Only 11 percent of consumers say contacting customer service is an enjoyable experience. Of those who are dissatisfied, 63 percent would rather clean the toilet than contact a customer service team. Only 10 percent say their typical customer service experience is ‘excellent.’
• Customers feel like organizations don’t know them well enough:
Despite 87 percent of business decision makers believing they know their customers well, the vast majority of consumers feel differently. Just 23 percent of consumers say businesses understand them as a person and their customer service preferences ‘extremely well,’ while 63 percent think organizations should make getting to know them better their top priority.
• Poor customer service can cost businesses customers:
Seventy-seven percent of customers agree the standard of customer service they receive is a major determining factor in their brand loyalty. In addition, 89 percent say receiving poor customer service from a business damages their impression of the brand. Significantly, 75 percent also say they have previously stopped doing business with an organization because of poor customer service. Forty-four percent report that if they receive a negative customer service experience, they immediately stop the purchase and move to another vendor. Despite this, only 35 percent of business decision makers say they lose customers ‘all the time’ or ‘fairly regularly’ as a result of providing poor customer service.
• Customers know what they want:
Consumers highlighted specific areas of frustration within customer service -- providing businesses with a clear roadmap for improvement. Their top three frustrations include taking too long to receive service (82 percent), having to repeat themselves when switching between channels or agents (76 percent), and not knowing the status of the query (64 percent). When asked what made for a positive customer service experience, 59 percent agree that a quick resolution of their issue or question mattered most, followed by a need for knowledgeable service agents (48 percent) and a fast response (47 percent).
“Good customer service can be the difference between success and failure. This study tells us that organizations still have a long way to go before they are able to fully meet the expectations of their customers,” said Tom Libretto, chief marketing officer, Pegasystems. “The good news is that there is overall agreement on what matters most. Solutions are available to help businesses understand and proactively address customer issues, while also arming customer-facing staff with the tools they need to provide more contextual, relevant, and knowledgeable service. Customers win, employees win, and positive business outcomes are delivered as a result.
Jun 03, 2019 • Features • Jan Van Veen • management • moreMomentum • Burning Platform • Service Innovation and Design
Quite often, when talking with business leaders and clients, I hear the problem that the organization and its people are not that open to innovate and change as they already have good performance and there is no clear threat visible yet. They experience it as a lack of “sense of urgency”: there is no “burning platform” for innovation and change.
A common approach is to either wait until the situation gets worse or construct a (mini)crisis to increase and maintain a sense of urgency.
However, the question is:
• Do we really need a burning platform to innovate and change? And;
• What are the downsides to building change and innovation around a burning platform?
In this article I will share five reasons why a Burning Platform is bad for sustainable innovation and change.
Why a burning platform is bad for innovation?
1.You are too late
Typically, the trends which create threats or opportunities develop a long while before becoming an obvious burning platform. First, there are the first weak signals for a trend. At this time, it is still hard to accurately predict what will happen and when. Maybe different way signals are contradictory.
So often, these weak signals are being ignored by the majority. After some time, we see the first competitors moving, but actually also struggling to successfully address the threats of opportunities. Their initiatives seem to be failing. As a result, the majority still waits. Once the leading competitors are having their first successes and the trends become emerging, the burning platform becomes visible.
But now, the leading competitors have learned and built capabilities and can scale. While the lagging majority is still trying to find the right questions, let alone the right answers. They are dropping behind the leading pack in their industry. They are too late.
2. You get a deeper performance dip
The urgent situation of a burning platform means there is a critical situation which requires a rapid response and rapid results.
The topic is becoming increasingly dominant in the daily activities of everyone in the organisations. All hands on deck!
It starts distracting attention from the daily work of running the business. The overall performance will suffer more and longer than if the urgent can critical situation would have been prevented by innovation and change at a much earlier stage.
3. You disengage your valuable people
In general, a necessity to change – the burning platform – will create higher stress levels which will impact altitude and behaviour towards change. The more critical and urgent the necessity, the bigger the chances are for stress levels which will trigger defensive reactions like fight, flight or freeze.
Too often, we see the stress levels resulting in internal fights, pointing fingers, pushing problems to other teams and the best talents moving to other companies.
These are negative sentiments, which can be transformed into a positive and bonding sentiment within teams for a while, but not for long.
4. You miss the best solutions
The defensive fight, flight or freeze behaviour mentioned above, also triggers short term reactive thinking and blocks constructive and creative thinking.
When solutions require deeper analysis, being open to new types of solutions and require collaboration between different teams or department, this reactive short-term thinking is counterproductive.
The high level of stress increases the risks of not seeing the real problems or opportunities, not finding the right solutions and not doing what it really takes to get the results.
"It starts distracting attention from the daily work of running the business..."
5. You increase the risk for failure
During the first attempt of implementing a new solution, we should expect hiccups. Instead of experiencing this as a failure, everyone should see this as learning.
They should be able to have a constructive and forward-looking mindset to collectively understand why it is not working yet and what interventions are required to get it right. With a flight, fight or freeze attitude, the chances are bigger people will blame others or the conditions, find reasons to justify the disappointing results and give up.
For sure, we know about success stories where companies successfully pivoted their business during a crisis, like IBM. We also now the examples where companies miserably failed during a crisis and did not survive.
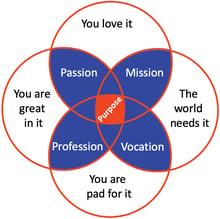
The better alternative: Purpose
The better alternative is what the leading and dynamic manufacturers do very well: the rally their employees, their clients and their partners with a strong and compelling purpose which makes continuous innovations and change the natural, logical and compelling thing to do.
Like everyone at Philips Healthcare is committed to transforming our healthcare by offering and developing integrated solutions (hardware, software, services) for people to live healthier, prevent deceases, be diagnosed quicker and more accurately, receive better and less intrusive treatment and receive the care they need at home.
Or like Tesla is accelerating the transition of sustainable energy and transportation with electric vehicles, better batteries and solar panels. This approach will be more rewarding for everyone, lead to sustainable success of the business and reduce the chances of entering periods of critical decline of performance. It will avoid you being on a burning platform.
The Essence: People Do change!
I believe that people do change and drive innovation, if there are compelling reasons and not too many obstacles. After all, that is the only reason the world is changing so rapidly.
Too many organisations do a bad job in providing compelling reasons and good job in creating obstacles. That is the reason organisations struggle in keeping up the high pace of changing world.
Leading, dynamic and innovative companies set themselves apart by maintaining a clear and compelling purpose, direction and strategic intent as well as e great environment for collaborative change and innovation.
Conclusion and recommendation
In this article, I described five reasons why the common practice burning platforms and sense of urgency are bad for innovation and change. I also briefly described the best practice alternative: build and maintain a compelling purpose for everyone to be proud of and to work on.
If you are on the same page and would like to take next steps, I would recommend you to:
• Assess what your personal view is on the reason your business or department should change and innovate differently or quicker.
• Assess to how compelling this is for the 1) shareholder, 2) boardroom, 3) employees and 4) clients.
• Evaluate and enrich (your view of) the purpose of your company or your department. What is your relevance for the industry, for your clients and for the society?
• Reach out to me for a discovery or sound-boarding session. I am happy to help and also curious to learn from your experience.
I am confident this will bring you actionable insights for your department - if not for the business as a whole. Good luck!
Jan van Veen is Founder and Managing Director at moreMoumentum.
May 29, 2019 • News • management • Cyber Security • insurance
In November last year, Mactavish published a report entitled ‘Cyber Risk & Insurance Report’, which identified eight common flaws in cyber insurance policies. This includes, for example, cover being limited to events triggered by attacks or unauthorised activity and excluding cover for issues caused by accidental errors or omissions.
Another flaw is only providing systems interruption cover for the brief period of actual network interruption, as opposed to the more significant knock-on revenue impact during the period after IT systems are restored but the business is still disrupted. In the last two weeks alone Mactavish has reviewed cyber insurance policies for a large British business and a medium sized business. Both of these policies had three or more of the flaws. Mactavish warns that despite insurance industry denials, the eight flaws are widespread.
Bruce Hepburn, Chief Executive Officer, Mactavish, commented: “Many in the industry have challenged our findings but we continue to find these issues affecting the actual policies we review that are being offered to UK businesses, and we will be publishing a second paper on the sector next month providing more details on our findings. “However, in the meantime, we are calling on brokers to challenge insurers more on the quality of the cyber cover they provide and push for improvements. If they can’t achieve this, they need to warn their clients of the omissions in their policies to give them a better understanding of what they are buying.”
Mactavish has issued a challenge to insurers and brokers to guarantee that the eight common flaws it has identified in policies will never be used as reasons to refuse pay-outs on cyber insurance claims unless they can show that a client has been informed but decided not to buy the additional cover. The eight flaws outlined in the Mactavish Cyber Risk & Insurance Report are:
1. Cover can be limited to events triggered by attacks or unauthorised activity – excluding cover for issues caused by accidental errors or omissions;
2. Data breach costs can be limited – e.g. covering only costs that the business is strictly legally required to incur (as opposed to much greater costs which would be incurred in practice);
3. Systems interruption cover can be limited to only the brief period of actual network interruption, providing no cover for the more significant knock-on revenue impact in the period after IT systems are restored but the business is still disrupted;
4. Cover for systems delivered by outsourced service providers (many businesses’ most significant exposure) varies significantly and is often limited or excluded;
5. Exclusions for software in development or systems being rolled out are common and can be unclear or in the worst cases exclude events relating to any recently updated systems;
6. Where contractors cause issues (e.g. a data breach) but the business is legally responsible, policies will sometimes not respond;
7. Notification requirements are often complex and onerous;
8. Businesses are forced to choose IT, legal or PR specialists appointed by their insurer.
May 17, 2019 • Features • future of field service • Jan Van Veen • management • moreMomentum • Digitalization • Servitization • The Field Service Podcast
In the latest Field Service Podcast, Jan Van Veen discusses why manufacturers unable to innovate their business model risk falling behind their competitors.
In the latest Field Service Podcast, Jan Van Veen discusses why manufacturers unable to innovate their business model risk falling behind their competitors.
In this special episode, Deputy Editor Mark Glover, speaks to moreMomentum's Jan van Veen who urges firms to take advantage of servitization and digitilastion and avoid stagnant business as usual behaviours.
Click here for material complimenting Jan's podcast including diagrams and charts. You can also contact Jan about any of the content raised in this recording and to find out how to get involved in Jan's new book, mentioned in the podcast, then click here.














 Field Service News is published by 1927 Media Ltd, an independent publisher whose sole focus is on the field service sector. As such our entire resources are focused on helping drive the field service sector forwards and aiming to best serve our industry through honest, incisive and innovative media coverage of the global field service sector.
Field Service News is published by 1927 Media Ltd, an independent publisher whose sole focus is on the field service sector. As such our entire resources are focused on helping drive the field service sector forwards and aiming to best serve our industry through honest, incisive and innovative media coverage of the global field service sector.
Leave a Reply