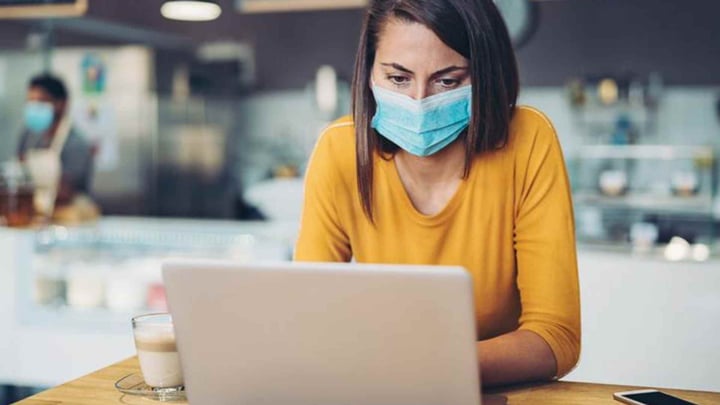
Mobile workforce using public Wi-Fi and unsecured home networks is a serious security hazard, warns cybersecurity expert.
ARCHIVE FOR THE ‘covid-19’ CATEGORY
Jan 10, 2022 • News • Cyber Security • Digital Transformation • remote working • Covid-19 • GLOBAL • Nordlayer
Mobile workforce using public Wi-Fi and unsecured home networks is a serious security hazard, warns cybersecurity expert.
The pandemic forced millions of workers to leave their offices and work remotely, creating new cybersecurity challenges for companies globally.
Cybercriminals took notice, causing companies to experience record-setting losses brought about by data breaches.
However, remote work is not a passing phenomenon - according to Gartner, 51% of knowledge workers will work remotely by 2022, which is a 24% increase when compared to 2019.
If remote work meant working from home at the beginning of the pandemic, it is now changing towards working from anywhere. Cybersecurity-wise, this means that an increasing number of workers will access their work networks through vulnerable networks, and additional security measures have to be put in place to mitigate the connected risks.
WFA: the dangers of public Wi-Fi and unsecured remote locations
The switch to home offices left managers dealing with several cybersecurity threats stemming from unsecured home devices and networks, as well as unprotected internet traffic.
When the majority of employees work from a single location, there is only a need to protect the main network - which is less demanding than protecting as many endpoints as there are employees.
The problem becomes even more evident once employees are not working from a fixed location like home but are, for example, traveling while working and have no choice but to use public internet access.
"Adapting to working from home was a challenge to cybersecurity personnel everywhere, but the growing trend of working from anywhere entails a new set of threats to consider," said Algirdas Sakys, Information Security Manager at NordLayer. "Working from anywhere usually means using unencrypted public Wi-Fi, which can lead to information being intercepted, malware being distributed. There is an array of ways in which hackers exploit unsecured public networks, and businesses have to adapt their cybersecurity strategies accordingly."
The Castle-and-moat approach to cybersecurity is no longer viable
Since every remote employee is a potential threat to the integrity of a given company's data, businesses are shifting their cybersecurity strategies away from the castle-and-moat approach. Now, network security solutions based on the Zero Trust principle are replacing traditional, static defense strategies.
In the Zero Trust framework, the given network is protected by granting users and devices access to only those parts of the network that are essential to their task. In such a system, every user is authenticated before being allowed to access the needed data through an encrypted tunnel. Because of this, even if a device gets compromised, it can't cause network-wide damage.
Organizations that have Zero Trust-based system in place enhance their cybersecurity in three key areas: secure access, secure browsing, and increased cybersecurity training opportunities, added the NordLayer expert:
"First, a comprehensive security framework of this kind allows the remote employees to safely connect to the company network without putting the whole network at risk. Second, web browsing becomes considerably safer, allowing cybersecurity personnel to ensure employee browsing habits are not potentially harmful to the company. Finally, due to the automated nature of Zero Trust-based systems, managers gain more time to educate their personnel on best cybersecurity practices, which is crucial because defrauding humans is one of the chief enablers of successful cyberattacks."
Further Reading:
- Read more about Digital Transformation @ www.fieldservicenews.com/digital-transformation
- Read more about Cyber Security on Field Service News @ www.fieldservicenews.com/cyber-security
- Read more about the impact of COVID-19 on FSN @ www.fieldservicenews.com/covid-19
- Find out more more about NordLayer @ nordlayer.com/
- Learn more about NordLayer @ twitter.com/NordLayer
Dec 22, 2021 • News • UK • Small Medium Businesses • SMB • Covid-19 • Leadership and Strategy • EMEA • Fintech
Despite lingering anxieties about the pandemic and a variety of economic and commercial issues, the majority of SMEs believe it is now imperative to begin building back from the crisis.
Despite lingering anxieties about the pandemic and a variety of economic and commercial issues, the majority of SMEs believe it is now imperative to begin building back from the crisis.
They are ready to step up their business investment, with ambitious plans for recruitment, renewal of equipment and machinery, and both domestic and international expansion. Fintech business lender MarketFinance asked 2,000 SME owners across the UK about their outlook for 2022 and beyond, gauging their short and long-term plans for business investment and growth. MarketFinance has today released a comprehensive research report of its findings, which are summarised here.
Confidence
Analysis of the survey results has shown that business confidence amongst SMEs is improving, with many firms now focused on recovery and growth. With pandemic disruptions now largely settled, half of SMEs (48%) expect their turnover to stabilise or to increase over the next 12 months. Similarly, 50% of SMEs expect demand for their products or services to stabilise or to increase over the next six months. MarketFinance’s research has found that the majority of SMEs (63%) expect their business to grow over the next three years
Investment
With survival mode no longer a necessity and cash flow pressures beginning to ease, the vast majority of SMEs (70%) now feel confident enough to increase business investment over the next 12 months. A quarter of SMEs plan to hire new staff, while 24% expect to purchase new equipment and machinery. When asked how they were factoring borrowing into their investment plans, 23% of SMEs said access to a broader range of borrowing options could enable them to increase investment even further.
Borrowing
The research findings demonstrate that borrowing will play a key role in recovery and growth with 62% of SMEs saying that prudent borrowing could help them fund growth. However, three quarters (71%) of SMEs do not believe traditional banking products are the most obvious and convenient way to borrow for investment. Despite this lack of alignment between current finance needs and the options available through traditional routes, more than a third of SMEs (37%) are looking to take on new borrowing facilities.
Growth
With confidence high and a sense of having moved beyond recovery and into a new stage of growth, many businesses are looking forward to seizing a host of opportunities in 2022. Almost all SMEs surveyed (81%) plan to invest in sustainability, while 30% say they are considering merger and acquisition (M&A) activity in the year ahead – more than twice as many as those primarily focusing on organic growth (14%). Over a third of businesses (34%) say they already sell overseas, or have plans to begin doing so. That figure is highest amongst the largest businesses surveyed (turnover between £5m and £6.5m) but even amongst smaller enterprises significant numbers are focused on export.
Anil Stocker, CEO at MarketFinance, commented: “It’s clear that the business environment has shifted and SMEs are looking ahead with a quietly confident and cautiously optimistic view. UK businesses intend to ramp up growth through domestic and international expansion, digital transformation and even M&A activity. But as they reset their post-pandemic goals for a post-pandemic, they’ll need to be confident of their funding base.
Given that so many SMEs are looking outside of traditional routes in their search for finance, we’re particularly proud to have been accredited by the British Business Bank as one of the few alternative providers under The Recovery Loan Scheme. Schemes like the RLS are a golden opportunity for SMEs looking to gear up for growth, providing easily accessible funding at a lower cost across a wide range of products. We expect to see a large number of SMEs taking advantage of the scheme over the next 6 months as their growth and expansion efforts gain momentum and they invest in ambitious plans for 2022 and beyond.”
Further Reading:
- Read more about Leadership and Strategy @ www.fieldservicenews.com/leadership-and-strategy
- Read more about the impact of COVID-19 @ www.fieldservicenews.com/COVID-19
- Read more about Fintech on Field Service News @
- Learn more about Market Finance @ marketfinance.com
- Follow Market Finance on Twitter @ twitter.com/marketfinance
Dec 21, 2021 • Features • White Paper • OverIT • Covid-19 • Servitization and Advanced Services
In the last feature from a recent white paper we published in partnership with OverIT, we analyse the key aspects of migrating from a legacy system to a new FSM solution.
In the last feature from a recent white paper we published in partnership with OverIT, we analyse the key aspects of migrating from a legacy system to a new FSM solution.

This feature is just one short excerpt from a recent white paper we published in partnership with OverIT.
www.fieldservicenews.com subscribers can read the full white paper now by hitting the button below.
If you are yet to subscribe you can do so for free by hitting the button and registering for our complimentary subscription tier FSN Standard on a dedicated page that provides you instant access to this white paper PLUS you will also be able to access our monthly selection of premium resources as soo as you are registered.
Data usage note: By accessing this content you consent to the contact details submitted when you registered as a subscriber to fieldservicenews.com to be shared withOverIT, sponsor of this premium content, who may contact you for legitimate business reasons to discuss the content of this white paper, as per the terms and conditions of your subscription agreement which you opted into in line with GDPR regulations and is an ongoing condition of subscription.
There are two key aspects of migrating from a legacy system to a new solution. The first is project planning for the migration itself. The second is to understand the human aspect of change- management as we seek to ensure quick adoption of the new tools from our end users.
In the concluding part of this paper, we shall take a look at each of these
PLANNING AND INTERATIVE DESIGN ARE KEY TO A SUCCESSFUL MIGRATION
As with all significant projects, it is essential to establish a strong, robust, and well-considered planning period.
This planning process should include identifying the key personnel within the planning team and outlining a project timeline. Given the mission-critical nature of field service delivery and the growing importance of service delivery to broader business strategies, wherever possible, it is worth considering making the critical appointments of those who will be most crucial to this project a full- time focus for the duration of the migration.
Moving from one system to another in any aspect of the business is challenging. In field service operations, a dedicated team focused solely on making the migration process seamless could be the difference between successful adoption and rapid evolution within your service organisation and catastrophe that could push progress back by years.
It is also important to have voices with different areas of expertise within that project team. Viewing such migration as an IT-only implementation is flawed. Leaders should view it as a business improvement initiative. Therefore, stakeholders from field service operations and IT, with their respective expertise, should be included within the core team, with relative subject matter experience to bring to the table. Experts also recommend seeking input from other relevant stakeholders, especially end-users such as field engineers and technicians.
However, perhaps the most critical voice in the process should be those who have been through this process before.
The solution provider you select to work with will have gone through this migration process with other clients and will know the pitfalls to avoid and the shortcuts to success. Throughout this entire process, they should be there to help guide you as you move from your legacy system to their next-gen solution, so lean on them for support as much as possible. It may even be that they can connect you to a trusted systems integrator that knows about taking companies from your existing system to your new system. While an additional cost, such insight and expertise can be invaluable and pay for itself within a short amount of time as you begin to see a return on your investment in these more sophisticated FSM tools.
One thing to consider is that the more traditional approach to implementation, where such projects can be active for at least six months before even taking the first actual steps to roll-out, is becoming less and less common. Increasingly, companies are adopting a more rapid approach of multiple small iterations, focusing on rapid development, issue resolution, and redevelopment as a solution moves from a minimum viable product to complete an adoption in incremental phases.
Systems integrators or solutions providers have the opportunity to utilize the knowledge of their existing environment, future environment, and transition practices. In this way, teams are not just recreating what existed previously into a new system, but they are simultaneously taking advantage of the new capabilities and new processes that the system offers.
Finally, as you begin to move through iterations and towards an actual go-live date, thinking about training and deployment becomes critical.
Training is also a crucial aspect of the change management process, which we shall look at in the concluding section of this paper.
CHANGE MANAGEMENT MUST BE FOCUSED ON PEOPLE ABOVE ALL ELSE IF IT IS TO SUCCEED
In any technology implementation, effective change management is critical. However, the stakes are even higher in this context, where the technology implementation can lead to significant new processes and even new service strategies.
Therefore, following a well-established path to managing the human aspect of change management is vital. Some key considerations include:
Understand the Task Ahead
Change is hard, and without a clear definition of your goals and the challenges you face, managing any change effectively can be at best a complicated and drawn-out process and, at worst, an abject failure.
In fact, according to change management guru John Kotter, 70% of change management efforts fail. This is mainly due to a lack of preparation, a lack of understanding of best practices, or a combination of both. However, at the heart of every successful change management exercise, one maxim holds. Change Management is always about people.
Engage Individuals in Their Heads and the Heart
For a change management program to succeed, we must acknowledge that change is about individuals, not organisations. Organisational needs and requirements will drive the change, but individuals will implement it and determine its success.
Given this notion, we must next consider how individuals will react to change. Successful change management is as much about feeling as it is about thinking. Change management is one of the fundamental principles in the Kotter Change Management philosophy and is widely accepted to be an essential step on the change management journey.
Embrace the Principles of Influence
Robert Cialdini’s six principles of influence are certainly also worth considering when planning your change management program.
The Six Principles include:
• Reciprocity
• Commitment and consistency
• Social Proof
• Liking
• Authority
• Scarcity
These key principles of influence are widely utilised in sales and marketing as they are fundamental pillars of communication that we universally understand as humans.
So as you begin engaging with your team around the changes you are introducing, a firm grounding in Cialdini’s principles can be a tremendous tool to have in your communications kit.
The Importance of the Change Agent
Building on the point above, by working with change agents, you will establish internal champions within the field workforce that can encourage widespread quick adoption amongst peers.
Gartner’s Elise Olding neatly sums up this approach stating, “Change resistance is a myth. Employees support enterprise goals when they understand what needs to be done. Change Agents put a face on change and leverage trusted informal leaders to create understanding among employees and influence organisational change.”
Breaking Down the Barriers of Resistance
The goal of a successful change management program should not be to eradicate resistance to change completely- this is an impossible task that will take too much energy.
Instead, focus on reducing the impact of resistance and overcoming it as quickly as possible to move the change management project from concept to full adoption as swiftly as possible.
The true key to successful change management is minimising the impact of resistance in your workforce- and to achieve this, we must understand the types of resistance we are likely to encounter.

This feature is just one short excerpt from a recent white paper we published in partnership with OverIT..
www.fieldservicenews.com subscribers can read the full white paper now by hitting the button below.
If you are yet to subscribe you can do so for free by hitting the button and registering for our complimentary subscription tier FSN Standard on a dedicated page that provides you instant access to this white paper PLUS you will also be able to access our monthly selection of premium resources as soo as you are registered.
 Data usage note: By accessing this content you consent to the contact details submitted when you registered as a subscriber to fieldservicenews.com to be shared with the listed sponsor of this premium content OverIT who may contact you for legitimate business reasons to discuss the content of this white paper, as per the terms and conditions of your subscription agreement which you opted into in line with GDPR regulations and is an ongoing condition of subscription.
Data usage note: By accessing this content you consent to the contact details submitted when you registered as a subscriber to fieldservicenews.com to be shared with the listed sponsor of this premium content OverIT who may contact you for legitimate business reasons to discuss the content of this white paper, as per the terms and conditions of your subscription agreement which you opted into in line with GDPR regulations and is an ongoing condition of subscription.
Further Reading:
- Read more about Servitization & Advanced Services @ www.fieldservicenews.com/servitization-and-advanced-services
- Read more about Digital Transformation @ www.fieldservicenews.com/digital-transformation
- Learn more about the impact of COVID-19 in the Field Service Industry @ www.fieldservicenews.com/covid-19
- Read more about OverIT on Field Service News @ www.fieldservicenews.com/exel
- Learn more about OverIT @ www.overit.it
- Follow OverIT on Twitter @ twitter.com/OverITSpA
Dec 17, 2021 • News • fleet management • UK • Covid-19 • Managing the Mobile Workforce • EMEA • VIMCAR
UK small and medium sized food businesses are feeling the pressure for customer deliveries in the lead up to Christmas, according to new research released by Vimcar.
UK small and medium sized food businesses are feeling the pressure for customer deliveries in the lead up to Christmas, according to new research released by Vimcar.Over half of those surveyed have experienced an increased demand for food deliveries in the lead up to Christmas compared with the last two years.
This pre-Christmas rush is putting clear pressure on deliveries and demand on fleets, with almost 90% of those surveyed offering a delivery service for their customers. A need which has been galvanised by a change in customers’ purchasing habits since the start of the pandemic, with many now expecting delivery options to be available as standard, rather than as an additional option.
OVER HALF OF FOOD DELIVERY BUSINESSES ARE EXPERIENCING A HIGHER DEMAND FOR DELIVERIES THIS CHRISTMAS, COMPARED TO THE LAST TWO YEARS
Undertaken by Vimcar, the fleet management software for SMEs, the survey comes at a time when food retailers are needing to increase their fleet size (93%) to keep up with demand, but are grappling with the impact of delivery driver shortages. Furthermore, almost all (96%) food businesses currently running fleets to fulfil delivery needs, expect their costs to increase between now and Christmas.
Despite the increased pressure and challenges facing SME food retailers, the majority of respondents (78%) are feeling optimistic about business performance for the Christmas period 2021, as a result of the increase in demand and the lifting of COVID restrictions in comparison to 2020.
Sami Eric, UK Country Manager at Vimcar said: “It is really uplifting to see that small and medium sized food retailers are thriving in the run up to Christmas, especially after a very challenging couple of years. With these higher demands comes higher expectations for businesses to meet. This research shows the challenges that the food industry is facing during the busiest time of the year, and the need for customers to be understanding of the changing landscape to which businesses are adapting to.”
Eric added: “As pressure mounts, efficient fleet management will be crucial in helping SMEs to offset rising fleet costs as well as maximise the investment they have made into new delivery services. Poorly managed fleets and drivers can quickly drain a business’ costs and resources, so implementing a fleet management tool is vital to simplify time spent on fleet admin and maintenance.”
Further Reading:
- Read more about Managing the Mobile Workforce @ www.fieldservicenews.com/managing-the-mobile-workforce
- Read more about Fleet Management @ www.fieldservicenews.com/fleet-management
- Learn more about Vimcar @ vimcar.co.uk
- Find our more about Aircargo Transport @ www.aircargo-transport.eu
- Follow Vimcar on Twitter @ twitter.com/goVimcar
Dec 14, 2021 • Features • White Paper • OverIT • Covid-19 • Servitization and Advanced Services
In the second feature from a white paper we recently published in partnership with OverIT, we take a look at what tools are included in the new FSM solutions and how they have evolved from the previous iteration of FSM software that we are currently...
In the second feature from a white paper we recently published in partnership with OverIT, we take a look at what tools are included in the new FSM solutions and how they have evolved from the previous iteration of FSM software that we are currently using.

This feature is just one short excerpt from a recent white paper we published in partnership with OverIT.
www.fieldservicenews.com subscribers can read the full white paper now by hitting the button below.
If you are yet to subscribe you can do so for free by hitting the button and registering for our complimentary subscription tier FSN Standard on a dedicated page that provides you instant access to this white paper PLUS you will also be able to access our monthly selection of premium resources as soo as you are registered.

Data usage note: By accessing this content you consent to the contact details submitted when you registered as a subscriber to fieldservicenews.com to be shared withOverIT, sponsor of this premium content, who may contact you for legitimate business reasons to discuss the content of this white paper, as per the terms and conditions of your subscription agreement which you opted into in line with GDPR regulations and is an ongoing condition of subscription.
Having laid out the case that we are now entering a new era of field service, one which will fully harness the technologies and tools embedded within next-generation FSM solutions, let us now take a look at what tools are included in such systems and how they have evolved from the previous iteration of FSM software that is currently in place.
DATA INTEGRATION
Field service has always been a complex beast with many moving parts. However, modern field service in some respects is more complicated than ever due to the various systems of record (SOR) that may be in place. In previous iterations of FSM solutions, all too often, field service operations remained in a silo. Today, however, the benefit and value of widely available data flow across multiple business units are becoming increasingly acknowledged.
Therefore, there must be the potential to import and export data from one system to another within any modern FSM solution. Whether feeding into a CRM for sales, an ERP for resource planning, or even into a SOR that sits across production and R&D to drive forward product improvements, easy integration across non-service focused systems is critical.
GIS CAPABILITIES / INTEGRATION
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) has become an increasingly important part of many field service organizations workflows. However, while incredibly valuable, GIS data may come from multiple data sources, potentially stored in different SORs.
In the fast-moving world of field service, particularly if we are looking at reactive emergency response scenarios, then the ability to surface data from multiple sources both in the back office and, most notably for the engineer in the field, is crucial.
Although inclusion of GIS capability within next-gen FSM solutions like Geocall is relatively new, this practice is happening more frequently and will likely become the standard. While this may not be relevant for every industry vertical, within specific sectors such as Oil and Gas or Utilities, this could be a real game- changer that we will see emerge in the FSM 3.0.
SCHEDULING OPTIMIZATION
The old mantra of getting the right engineer, with the right skills, to the right job, at the right time will never fade as being the most central tenet of field service management and indeed service delivery as a whole. Across the last decade, we have seen tremendous strides made in scheduling with various approaches such as truly dynamic optimized scheduling and Darwinian algorithm-based scheduling. Such algorithm-based scheduling is paving the way for the increasingly widespread adoption of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and AI leveraging the support of field service processes.
However, such sophisticated solutions are not always the right choice for each company or even for each type of service a single organization may have within its portfolio. The more sophisticated solutions are fantastic, for example, in dealing with large-scale service workflows, with large teams of field service engineers. They are also exceptionally effective in scenarios where there
may be complex requirements to place the right combination of skills across multiple engineers to meet the needs of the job.
In each of the above scenarios, we could see a different use case. In the first scenario, we could view an optimized scheduling engine as an opportunity to automate much of the dispatch workload, allowing the service organization to place human resources in roles that are more aligned to revenue generation than cost reduction. In such an instance, the human dispatcher adopts the role of supervisor. For example, ensuring the automation process is handling 80% of calls within standard parameters while taking control of the 20% that require a more nuanced approach (in line with the Pareto or 80:20 rule).
In the second scenario, where such a nuanced understanding of a more complex service scenario is required, we may consider assisted scheduling rather than automation.
The flexibility to have both solutions covered within a next-gen FSM solution is essential. However, what differentiates the new breed of FSM solution to many of the older legacy solutions is that scheduling tools, whether fully automated or assisted scheduling, should now always be expected to be dynamic. A dynamic solution can react to real-time data from the field, including engineer updates, traffic information, and customer data. This is a crucial aspect of next- gen solutions and allows for the work schedule to be constantly optimized.
EFFECTIVE REPORTING TOOLS
As we discussed earlier in the paper, the importance of data flowing between your FSM and other SOR has never been more critical. Service operations are now becoming a key driver in multiple core aspects of the broader business operations, and as such, the flow of information across the business must be seamless. Directly aligned to the importance of that data flow moving beyond the traditional silos is the ability for data to be surfaced in an easy yet meaningful way.
Within the context of next-gen FSM solutions, this primarily relates to dashboards that can be customizable for various levels of management allowing them to see the data in the manner they need. Modern-day reporting should give us the tools to simultaneously cut out the background noise of data unnecessary to the job at hand while tapping into the vast data lakes that are the bi-product of modern-day service management and bringing to the fore the data insight that is of use. It is also an expectation of next-gen FSM solutions such as Geocall to utilize different algorithms to translate the data into multiple use cases.
To illustrate this, let us look at an example most field service leaders would be familiar with, capacity planning.
We may have several data sets that we utilize in our capacity planning, say operations metrics that give us mean-time-per-job and technician utilization time. Alongside this, we may have customer job schedule data by volume and location. Then we may also have historical asset data that outlines the complexity of a given task.
In a next-gen FSM solution, we can apply different scheduling models, which allows us to compare and contrast based on various priorities and parameters. In essence, it is a glimpse into the future to see what could work and what may not.
In one scenario, we could run a model based on equity distribution to apportion workload fairly across all resources. Alternatively, we may want to run the same data against a logistic optimization to try to reduce travel and reduce time and reduce cost for the business.
In either scenario, we may want to factor in contingency capacity to accommodate any emergency work that comes in to ensure we have appropriate resources available to offer our customers total service support whenever called upon.
This scenario is just a brief example of the importance of effective reporting tools for service operations. The ability for a service leader to ask, “I want to make a change, what’s the impact?” and to effectively model out the answer to that question is a cornerstone of next-gen FSM.
MOBILE CAPABILITY
As we mentioned earlier in this paper, one of the significant shifts from FSM 1.0 to FSM2.0 was the inclusion of mobile. In the current status quo there is widespread provision of mobile solutions in the iterations of FSM solutions. However, next-gen solutions greatly magnify the complexity of such elements.
It is critical here to note that the complexity should always remain under the bonnet. Ultimately, the more sophisticated the technology on offer is, the more intuitive and seamless the experience should be for the end-user.
With this in mind, the mobile app of 2021 looks very different from those we would see just a few years ago, which were often little more than glorified push notifications showcasing job updates.
A modern FSM embedded mobile app should empower the engineer to capture accurate materials or asset data. It should guide them through structured workflows based on the job at hand while pulling in data from the asset itself.
It should play a pivotal role in ensuring that health and safety standards are met every time by placing clear checklists that technicians must complete before releasing additional information to the engineer. It should allow for a seamless customer interaction process- from having direct access for the engineer to order parts required when on-site, through the automated dispatch of invoices on receipt of an e-signature.
And returning to our concept of making the point of service as seamless as possible, the very best modern systems can do so in a truly dynamic fashion.
In Geocall, for example, the screen presents a truly dynamic experience for the field engineer or technician. The mobile solution understands the type of operation being undertaken and the most appropriate associated forms to capture the required data. Hotlinks are provided to the most relevant information within the knowledge library. The potential to record a solution to a currently unlisted problem allows the service organization to improve their knowledge base continuously.
The longer technicians use this tool, the more powerful it becomes.
And perhaps the most essential element of all, when it comes to identifying modern FSM technology, is that the mobile app links seamlessly to a virtual collaboration tool
VIRTUAL COLLABORATION / AUGMENTED REALITY
In the first section of this paper, we touched on how one of the primary shifts we will see as the dust settles and the new normal of field service begins to crystallize, is the more extensive use and many forms of remote service delivery will continue.This will take many forms. It may become a tool that technicians use for empowering self-service and self-maintenance for the customer. Workers may utilize it as the first level of support and enhanced triage tool. It may also support engineers in the field should they face an issue new to them requiring guidance from a more experienced colleague.
There are numerous papers dedicated to remote service tools available already on www.fieldservicenews.com, which are essential reading for all service companies seeking to embrace this modern approach to service delivery.
As a result, we won’t dwell on the topic too much here in terms of the benefits and considerations of adopting such a mechanism for service delivery. However, in the context of this paper, suffice to say, remote or virtual service collaboration tools are perhaps one of the most essential ingredients of FSM 3.0.
“Remote Service delivery and asset connectivity, however, are the agents of digital transformation. They do not just allow us to take the same processes and optimize them; they will enable us to rethink processes entirely and redefine service delivery...”
Embedding a remote service tool within an FSM system is currently the hallmark of next-gen systems. Some solutions have embedded remote service capability such as SPACE1 solution, whereas others will utilise 3rd party solutions and are reliant upon API based integration, increasing complexity and overhead.
Such a solution allows the service provider to have an experienced pair of eyes on-site almost instantaneously. It allows the service organization to access a site environment to either triage the information or resolve the problem remotely.
In more sophisticated tools such as SPACE1, we see the emergence of an intelligence-led knowledge management approach. Improved knowledge management means that a service organization can field the correct information at the right time to the engineer or the customer on-site via the tool. At the same time, the data automatically passes through image recognition technology, so it can automatically tag the correct information to make it more easily found at a later point if needed.
Such tools allow for rich information capture, whether images, videos or audio, while being utilized on-site, so every aspect of the maintenance or repair is catalogued correctly. Cataloging allows it to be fed back into the knowledge base to be used again in the future or even provide supporting documentation for invoicing or warranty disputes.
Additionally, we are seeing the rise in such tools in both training and on- boarding and critically reducing the time it takes to bring an engineer into the team before becoming a productive member of the workforce.
While all of the above tools are key factors in why service organizations should now upgrade or replace legacy systems, remote service tools are very much the poster boy of modern FSM solutions.
Again, the comparison to how Cloud and Mobile dramatically changed the game in FSM 2.0 holds true. Remote service, alongside IoT, are two technologies that will be the hallmark of FSM 3.0 as Cloud and Mobile where previously.
While there are therefore apparent comparisons, there is, however, a distinct difference.
The introduction of Cloud and Mobile, were perhaps the high watermarks of digitalization, allowing us to improve upon the efficiencies of traditional field service management processes.
Remote Service delivery and asset connectivity, however, are the agents of digital transformation. They do not just allow us to take the same processes and optimize them; they will enable us to rethink processes entirely and redefine service delivery in a more optimal way for the customer and the service provider.

This feature is just one short excerpt from a recent white paper we published in partnership with OverIT..
www.fieldservicenews.com subscribers can read the full white paper now by hitting the button below.
If you are yet to subscribe you can do so for free by hitting the button and registering for our complimentary subscription tier FSN Standard on a dedicated page that provides you instant access to this white paper PLUS you will also be able to access our monthly selection of premium resources as soo as you are registered.
 Data usage note: By accessing this content you consent to the contact details submitted when you registered as a subscriber to fieldservicenews.com to be shared with the listed sponsor of this premium content OverIT who may contact you for legitimate business reasons to discuss the content of this white paper, as per the terms and conditions of your subscription agreement which you opted into in line with GDPR regulations and is an ongoing condition of subscription.
Data usage note: By accessing this content you consent to the contact details submitted when you registered as a subscriber to fieldservicenews.com to be shared with the listed sponsor of this premium content OverIT who may contact you for legitimate business reasons to discuss the content of this white paper, as per the terms and conditions of your subscription agreement which you opted into in line with GDPR regulations and is an ongoing condition of subscription.
Further Reading:
- Read more about Servitization & Advanced Services @ www.fieldservicenews.com/servitization-and-advanced-services
- Read more about Digital Transformation @ www.fieldservicenews.com/digital-transformation
- Learn more about the impact of COVID-19 in the Field Service Industry @ www.fieldservicenews.com/covid-19
- Read more about OverIT on Field Service News @ www.fieldservicenews.com/exel
- Learn more about OverIT @ www.overit.it
- Follow OverIT on Twitter @ twitter.com/OverITSpA
Dec 07, 2021 • Features • White Paper • OverIT • Covid-19 • Servitization and Advanced Services
Field service has changed dramatically in the last 18 months, although we were already on a path of development from one phase of our evolution to the next as an industry.
In the first excerpt from a recent white paper we published in partnership...
Field service has changed dramatically in the last 18 months, although we were already on a path of development from one phase of our evolution to the next as an industry.
In the first excerpt from a recent white paper we published in partnership with OverIT, we start looking at what we should expect from an FSM solution suited to the post-pandemic world and how do we map an effective path from our existing legacy solutions.

This feature is just one short excerpt from a recent white paper we published in partnership with OverIT.
www.fieldservicenews.com subscribers can read the full white paper now by hitting the button below.
If you are yet to subscribe you can do so for free by hitting the button and registering for our complimentary subscription tier FSN Standard on a dedicated page that provides you instant access to this white paper PLUS you will also be able to access our monthly selection of premium resources as soo as you are registered.

Data usage note: By accessing this content you consent to the contact details submitted when you registered as a subscriber to fieldservicenews.com to be shared withOverIT, sponsor of this premium content, who may contact you for legitimate business reasons to discuss the content of this white paper, as per the terms and conditions of your subscription agreement which you opted into in line with GDPR regulations and is an ongoing condition of subscription.
The pandemic alone didn’t distrupt how we approach service delivery, we had already planted the seeds some time ago. Undoubtedly, the pandemic accelerated our journey, but it pushed us faster down a path we were already on. It was the catalyst for change rather than the reason.
Servitization, for example, had already grown from a niche strategy to a mainstream concept discussed in service organization boardrooms around the world.
However, as we begin to see a clearer picture of the new normal, servitization is shifting from a nice to have to an essential strategic move for many companies.
Our post-pandemic world is one where we may begin to see a reversal of the drive to the globalization of the supply chain. Many manufacturers are still reeling from the disruption that was brought to their business by external factors. One solution is a more decentralized approach that, while proving more costly, would be far more robust should we face similar challenges once again.
Another external factor driving servitization is the focus on the circular economy becoming more pressing as we address climate change issues impacting us all. A focus on sustainability suddenly moves beyond nice- sounding PR. It is now an essential facet of how we, as an industry, must embrace bold thinking as we consider field service in such a context.
Servitization, for many companies, allows for shifting the responsibility of output to the service provider, leading by necessity to more intelligent design of assets that are designed to last longer and can be more easily maintained.
Similarly, with remote service delivery, we see external factors come into play that could shape its role in the future of service delivery. Remaining on the point of sustainability, for example, the ability to reduce the carbon footprint of the field workforce is hugely boosted by the adoption of remote service tools and technologies.
Yet, only a few years ago, remote service delivery was very much the domain of best-in-class leading-edge adopters. Today it is being embraced across our industry. Remote service delivery, an approach to maintenance that companies adopted mainly out of necessity during the times of lockdown, has shown us en masse that there could be another way of approaching service delivery, problem triage, and issue resolution.
These are two very brief examples of how the industry is currently going through a significant process of evolution, driven in part by factors outside of our control. However, ours is an industry that adapts well. Ours is an industry populated with problem solvers and forward thinkers, a natural result of the often linear progression from field engineer to management that many of our industry’s leaders have chosen to take.
Indeed, it was not that long ago that we went through a similarly significant shift, as service moved from cost-centre to profit centre for a majority of service organizations. Again, this shift was, at first, glance a reaction to external disruption. Many point back to the 2008 recession as a pivotal moment in that shift.
With the global economy fractured and product margins being pushed to paper-thin levels, we witnessed a focus on service both as a critical differentiator to win and retain business but also as a vital revenue generator.
This came at a time when CAPEX investment for new assets was scarce and a desire to sweat assets that much longer, was wholly reliant on strong service agreements. Yet, while the 2008 recession certainly played its part in shaping that phase of industry evolution, much like the ongoing uncertainties in both economic and other factors are doing today, that first decade of the new century showed individuals at the forefront of innovative service design focuisng on service as a profit center.
Equally, like today, that shift in thinking was inspired by and empowered by a wave of technological innovation. As much as Augmented Reality, the Internet of Things, and Artificial Intelligence are changing the way we approach service delivery moving forward now, both Cloud and Mobile Computing radically altered the idea of what was possible then.
If we think back to the systems that preceded that era, there was a basic foundational layer within those early FSM solutions that were built and expanded upon, thus creating a new generation of solutions.
Elements such as scheduling and engineer-orientated mobile applications were often best-of-breed solutions designed for one purpose that integrated into the FSM platform. Then as we began to see these elements become standard inclusions, we moved into an era of FSM2.0.
Similarly, we have now begun to see new technologies like remote assistance tools, AI-based triage, and next-generation dynamic scheduling move through maturation. These tools that were often external to the FSM solution are becoming embedded in sophisticated next-generation platforms such as Geocall from OverIT as we begin to see the emergence of FSM 3.0.
In this paper, we shall explore what we should expect from such solutions and outline some guidance on the migration from an existing legacy solution to a solution designed with the emerging challenges of the new normal in mind.

This feature is just one short excerpt from a recent white paper we published in partnership with OverIT..
www.fieldservicenews.com subscribers can read the full white paper now by hitting the button below.
If you are yet to subscribe you can do so for free by hitting the button and registering for our complimentary subscription tier FSN Standard on a dedicated page that provides you instant access to this white paper PLUS you will also be able to access our monthly selection of premium resources as soo as you are registered.
 Data usage note: By accessing this content you consent to the contact details submitted when you registered as a subscriber to fieldservicenews.com to be shared with the listed sponsor of this premium content OverIT who may contact you for legitimate business reasons to discuss the content of this white paper, as per the terms and conditions of your subscription agreement which you opted into in line with GDPR regulations and is an ongoing condition of subscription.
Data usage note: By accessing this content you consent to the contact details submitted when you registered as a subscriber to fieldservicenews.com to be shared with the listed sponsor of this premium content OverIT who may contact you for legitimate business reasons to discuss the content of this white paper, as per the terms and conditions of your subscription agreement which you opted into in line with GDPR regulations and is an ongoing condition of subscription.
Further Reading:
- Read more about Servitization & Advanced Services @ www.fieldservicenews.com/servitization-and-advanced-services
- Read more about Digital Transformation @ www.fieldservicenews.com/digital-transformation
- Learn more about the impact of COVID-19 in the Field Service Industry @ www.fieldservicenews.com/covid-19
- Read more about OverIT on Field Service News @ www.fieldservicenews.com/exel
- Learn more about OverIT @ www.overit.it
- Follow OverIT on Twitter @ twitter.com/OverITSpA
Nov 30, 2021 • News • delivery • fleet • eCommerce • Covid-19 • Managing the Mobile Workforce • EMEA • VIMCAR
In this article for Field Service News, Sami Eric, UK Country Manager at Vimcar, discusses the benefits of digitalisation in fleet management.
In this article for Field Service News, Sami Eric, UK Country Manager at Vimcar, discusses the benefits of digitalisation in fleet management.
With businesses looking to increase their fleets in the wake the Coronavirus pandemic, the pressure is on to efficiently and successfully keep track of any new vehicles added to growing fleets. In a recent survey by Vimcar, a quarter (24%) of fleet managers said they spend half their working day on spreadsheets, with almost half of fleet managers finding spreadsheet set up too time consuming and 37% say it leaves room for mistakes. What’s more, there are still some who have not made the switch to digital spreadsheets, as 10% of those surveyed are still using pen and paper to keep tabs on vehicles, drivers, regulations and more.
Those fleet managers using spreadsheets or pen and paper to track costs, etc. are clearly not utilising their data to analyse the efficiency of their fleets. Yet, according to thousands of key decision makers in a recent survey, 75% believe that ‘data plays an important role in underpinning business decision making’.
With the challenges facing business growth, including economic uncertainty, Brexit, driver shortages, changes in road regulations and emission charges, there is a need for fleet managers to utilise data effectively in order to keep track of the numerus changes unfolding and make key business decisions. Efficiency and accuracy are crucial, and without it, problems arise. But the benefits of streamlining fleet management processes will go beyond efficiency and time saving.
WHY FLEET MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE IS SO IMPORTANT
Fleet management software is a broad term that describes the work required to keep fleet vehicles safe and operational at all times. Unexpected vehicle breakdowns, unplanned trips and hefty fines for expired vehicle documentation are all common fleet management issues that can be solved with more efficient ways of fleet tracking, which is often part of fleet management software. Modern tools that draw on data analysis gives a more in-depth knowledge of how a fleet is running and makes it easier to spot any potential issues ahead of time. Businesses that are still using paper logs to track their fleet are at a much larger disadvantage and run the risk of overlooking vehicle document renewal deadlines, misplacing mileage logs and more.
With the current issues around HGV driver shortages, fleet management is proving to be even more vital for companies keeping up with increased customer demands. As a temporary solution to the driver shortage, the government relaxed the HGV driver’s hours rules, meaning drivers can increase their daily driving limit from 9 hours to 11 hours twice a week. However, it’s up to each company to ensure drivers are properly tracking and sticking to their hours.
The problem is that many companies lack proper oversight of their drivers’ movements, and few can afford steep fines from incompliance. Plus, when you don’t monitor drivers, resources inevitably get wasted. And during a driver shortage, efficiency is essential.
THE DIGITAL SWITCH AND ITS BENEFITS
SMEs that have not yet digitalised their fleet are at a significant disadvantage compared to those who have. Without fleet management software, it’s impossible to tell where each driver is and whether they’re running on time or within the desired driving hours. That also means customers can’t be provided with accurate ETAs, nor can they be given concrete proof of delivery or pickup.
Without this digital software, fleet managers have to monitor driving hours with manually-filled mileage logs, which take longer to go through and are easily misplaced. With fleet management software, users are able to optimisie drivers’ routes, which not only reduces travel time, but also helps to decrease fuel expenses and optimise driving behaviour.
Vimcar’s survey found that 1 in 3 SMEs digitalised their fleet during the Covid pandemic. Of those, 94% agreed that adopting more technology has directly benefited their business by making services more efficient, improving the customer experience and it making employees’ lives easier.
As the pressure grows for business of all sizes to continue to build back, whilst maximising efficiency and satisfying customers’ demands for deliveries, using data to provide insights and analysis on how fleets are performing is key. With clarity comes efficiency, but also helps to relieve the stress from fleet managers and drivers, when a fleet is well managed and under control.
TIPS AND TACTICS TO SUPPORT THE SWITCH FROM EXCEL TO A FLEET ADMIN TOOL
- Tracking vehicle hours: If you know how long a vehicle is booked for, you know how long it will be driven for and which driver you need to follow up with if they do not drive the hours specified.
- Fuel consumption: Ensure your fleet management software supports the fuel card you use. This makes it much easier to keep track of fuel costs, which are undoubtedly one of the biggest expenditures for a fleet.
- Take time upfront to input important dates and tasks: Regular tasks and deadlines such as contract expirations or MOTs can quickly creep up when they are not properly managed. By taking the time at the start to input this data will not only save a lot of time in the long run but will ensure you never miss an important deadline.
- Get the guidance you need: Make sure your fleet software provider takes the time to walk you through the software – either in person or remotely. This will give you a good understanding of how each aspect of the software works and will allow you to make the most of all of its functionality. At the very least, be sure your provider has a high level of customer service so if you do have any questions you can get through to someone easily.
- Automated workflows: Where possible, set up automated workflows to help save time, allow real-time improvements to your fleet and give you reduce running costs.
Further Reading:
- Read more about Managing the Mobile Workforce @ www.fieldservicenews.com/managing-the-mobile-workforce
- Read more about Fleet Management on Field Service News @ www.fieldservicenews.com/fleet-management
- Learn more about Vimcar @ vimcar.co.uk
- Connect with Sami Eric on LinkedIn @ www.linkedin.com/in/sami-eric
- Follow Vimcar on Twitter @ twitter.com/goVimcar
Nov 25, 2021 • Features • Digital Transformation • Aquant • Covid-19 • customer experience
Aquant, has recently published the 2022 Service Intelligence Benchmark Report, now available at Field Service News, which offers an in-depth analysis of field service performance and customer satisfaction in a year of talent shortage, COVID service...
Aquant, has recently published the 2022 Service Intelligence Benchmark Report, now available at Field Service News, which offers an in-depth analysis of field service performance and customer satisfaction in a year of talent shortage, COVID service pivots, and shifting customer demands. In this final excerpt from the report, we discuss how companies can look beyond KPIs.

This feature is just one short excerpt from a report published by Aquant
www.fieldservicenews.com subscribers can read the full report now by hitting the button below.
If you are yet to subscribe you can do so for free by hitting the button and registering for our complimentary subscription tier FSN Standard on a dedicated page that provides you instant access to this white paper PLUS you will also be able to access our monthly selection of premium resources as soo as you are registered.
 Data usage note: By accessing this content you consent to the contact details submitted when you registered as a subscriber to fieldservicenews.com to be shared with the listed sponsor of this premium content Aquant who may contact you for legitimate business reasons to discuss the content of this white paper, as per the terms and conditions of your subscription agreement which you opted into in line with GDPR regulations and is an ongoing condition of subscription.
Data usage note: By accessing this content you consent to the contact details submitted when you registered as a subscriber to fieldservicenews.com to be shared with the listed sponsor of this premium content Aquant who may contact you for legitimate business reasons to discuss the content of this white paper, as per the terms and conditions of your subscription agreement which you opted into in line with GDPR regulations and is an ongoing condition of subscription.
The Customer Experience Gap
The Customer Experience Gap shows the difference between what customers expect and what your organization delivers.
Our analysis shows that companies who measure FTF rates in 7-day or 14-day windows are setting the stage for a wide experience gap—which leads to frustrating customer experiences. The moral of the story: a few metrics can’t provide the entire picture. It’s time to look at experience as a whole.
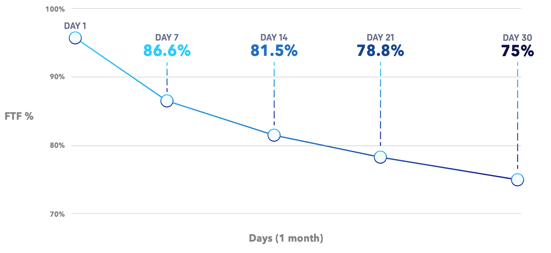
Instead of defining FTF in arbitrary time increments (7 days, 14 days, or 21 days), think about it in terms of the natural service cycle. Our research shows that measuring in 30-day windows strips out false-positive FTF rates.
Understand where your organization falls on the Customer Experience Gap chart.
- If your FTF rate is similar when measured at 7 days and 30 days, you have a small gap.
- If your FTF rate has a wide variation (usually a high rate at 7 days and a low rate at 30 days), you have a large gap.
- If you have a large gap, your team is focused on hitting their numbers instead of focusing on great customer experiences.
Why FTF Rates Vary by Time
When measured in short windows (like 7-day increments), jobs where a technician made an incorrect fix—but got the machine to work temporarily—will be marked as complete. But an incorrect fix is only a temporary measure, and the machine will continue to break down until properly repaired. For instance, a customer may call for service two or three times in a 30-day window. If you only measure in 7-day increments, your dashboard may show you successfully completed three jobs for one customer. In reality, these were three failed visits. This environment also leads to customer escalations and customer complaints that management may deem as “surprise complaints” that they didn’t see coming.
When it comes to service, it’s just as important to maximize the time between events and failures as it is to fix things correctly the first time. The less a customer needs a technician on-site, the better. This means the customer’s needs are being met.
Two Examples of Poor Customer Experiences
Company A: KPIs are not aligned to customer outcomes
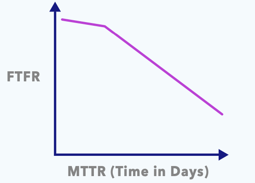
When FTF curves start out flat, it means that the company likely incentivizes high FTF rates over deep problem-solving. That’s shown by the curve getting steeper at the end of a 30-day cycle, indicating that the FTF rate is plummeting.
The key takeaway: Company A is not closely monitoring FTF rate—or there is no incentive to maintain a high rate over a long period of time—leading to poor customer experiences.
Company B: KPIs are not aligned to customer outcomes
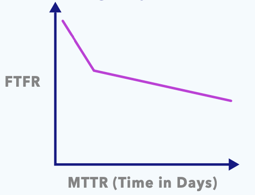
Here, the FTF rate starts out high and eventually flattens out. This may indicate that more preparation, information, or triage was needed before visiting a job site. A return visit would most likely be required to successfully solve the problem. Unlike Company A, Company B eventually solves root problems, but it requires several visits.
The key takeaway: Company B is trying to provide great customer service, but has some limitations that hinder quick and accurate outcomes, such as a lack of prep or an employee knowledge gap.
The Skills Gap - A Profile of the Top and Lowest Performing Organisations
What does the knowledge gap have to do with hitting KPIs?
If there is a large knowledge gap between team members, performance will vary—and so will customers’ experiences. That’s why it’s crucial to make sure that your technicians are equally knowledgeable about the equipment that they service and up-to-date on specific customer preferences.
Determine your team’s skills gap.
To increase your team’s knowledge and success, you must first identify how much of a gap exists between your star technicians (heroes) and underperformers (challengers).
For this report, we calculated the percentage difference between heroes and challengers across all organizations on the following page. We divided it into:
- Above average organizations
- Above performing organizations
- Below average organizations
A Snapshot of high performing and low performing organizations
The top 20% of organizations have a smaller workforce skills gap. A workforce with a more equal knowledge distribution results in more consistent customer experiences.
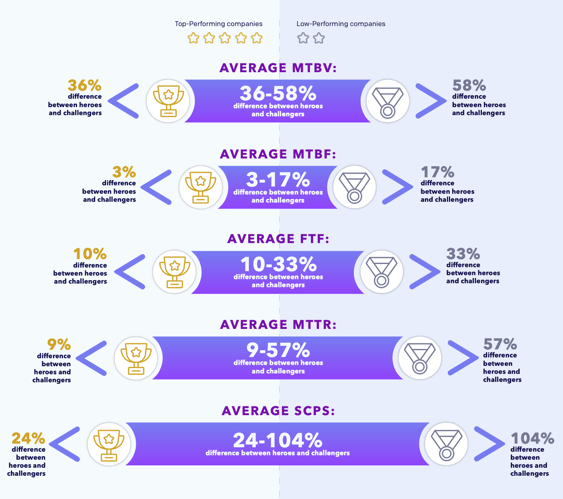
Why the Skills Gap Matters
A bigger distance between heroes and challengers leads to:
- Decrease in customer satisfaction
- Increased workload on your already overburned experts
- Increase in service costs
- Less capacity for organizational resilience
- Negative impact on growth
What's Next?
The service industry is facing unprecedented workforce shortages and increasing customer demands. A better way to overcome these challenges is to understand your business on a much deeper level than you do today so you can tailor service for every customer. Here’s where to start.

This feature is just one short excerpt from a report published by Aquant.
www.fieldservicenews.com subscribers can read the full report now by hitting the button below.
If you are yet to subscribe you can do so for free by hitting the button and registering for our complimentary subscription tier FSN Standard on a dedicated page that provides you instant access to this white paper PLUS you will also be able to access our monthly selection of premium resources as soo as you are registered.
 Data usage note: By accessing this content you consent to the contact details submitted when you registered as a subscriber to fieldservicenews.com to be shared with the listed sponsor of this premium content Aquant who may contact you for legitimate business reasons to discuss the content of this white paper, as per the terms and conditions of your subscription agreement which you opted into in line with GDPR regulations and is an ongoing condition of subscription.
Data usage note: By accessing this content you consent to the contact details submitted when you registered as a subscriber to fieldservicenews.com to be shared with the listed sponsor of this premium content Aquant who may contact you for legitimate business reasons to discuss the content of this white paper, as per the terms and conditions of your subscription agreement which you opted into in line with GDPR regulations and is an ongoing condition of subscription.
Further Reading:
- Read more about Aquant on Field Service News @ www.fieldservicenews.com/aquant
- Read more about Digital Transformation @ www.fieldservicenews.com/digital-transformation
- Read more about Leadership & Strategy @ www.fieldservicenews.com//leadership-and-strategy
- Learn more about Aquant @ www.aquant.io
- Follow Aquant on Twitter @ twitter.com/Aquant_io
Nov 18, 2021 • Features • Digital Transformation • Aquant • Covid-19 • customer experience
Aquant, has recently published the 2022 Service Intelligence Benchmark Report, now available at Field Service News, which offers an in-depth analysis of field service performance and customer satisfaction in a year of talent shortage, COVID service...
Aquant, has recently published the 2022 Service Intelligence Benchmark Report, now available at Field Service News, which offers an in-depth analysis of field service performance and customer satisfaction in a year of talent shortage, COVID service pivots, and shifting customer demands. In this excerpt from the report, we look at what KPIs do and don't tell us.

This feature is just one short excerpt from a report published by Aquant
www.fieldservicenews.com subscribers can read the full report now by hitting the button below.
If you are yet to subscribe you can do so for free by hitting the button and registering for our complimentary subscription tier FSN Standard on a dedicated page that provides you instant access to this white paper PLUS you will also be able to access our monthly selection of premium resources as soo as you are registered.
 Data usage note: By accessing this content you consent to the contact details submitted when you registered as a subscriber to fieldservicenews.com to be shared with the listed sponsor of this premium content Aquant who may contact you for legitimate business reasons to discuss the content of this white paper, as per the terms and conditions of your subscription agreement which you opted into in line with GDPR regulations and is an ongoing condition of subscription.
Data usage note: By accessing this content you consent to the contact details submitted when you registered as a subscriber to fieldservicenews.com to be shared with the listed sponsor of this premium content Aquant who may contact you for legitimate business reasons to discuss the content of this white paper, as per the terms and conditions of your subscription agreement which you opted into in line with GDPR regulations and is an ongoing condition of subscription.
WHAT KPI MEASUREMENTS DO AND DON'T TELL US
KPIs don't equal customer sentiment
In the Service Leader’s Guide to Workforce KPIs, we examined why workforce measurement is more critical than ever, and we defined best practices for measurement criteria.
For the 2022 Service Intelligence Benchmark Report, we went a step further. We analyzed service data to understand service performance beyond KPI measurement. We found that knowing your KPIs—by number or average performance—is not the same as understanding what those numbers reveal about customer satisfaction, employee skill level, or overall service performance. Averages don’t disclose the specific details you need to make critical service decisions.
Service KPIs by the numbers
Here’s the breakdown of how service organizations measure up against other organizations and the industry as a whole.
FTFR - First Time Fix Rate
What is it?
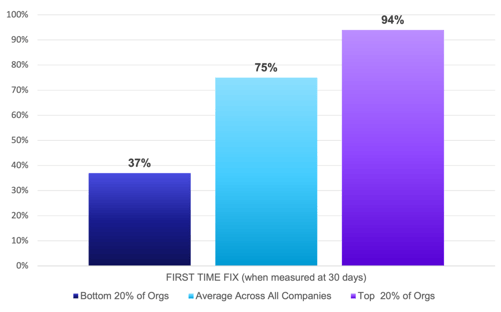
First Time Fix rate is one of the most popular metrics for workforce measurement. It indicates how often someone is able to fix an issue on the first try. In this report, we are measuring the FTF rate of field visits, in a 30-day window.

Key Observation:
FTF rates have hovered around 75% for more than a decade—and remained stagnant for all but a handful of top-performing companies. Additionally, FTF rates should never be measured in isolation. On average, a failed first visit leads to 2.5 additional visits and 20 days for MTTR.
CPS - Cost Per Success
What is it?
The total amount required to successfully close a service ticket is known as the Cost Per Success (CPS). This is a bit different from other similar-sounding KPIs, such as Cost Per Truck Roll, since total CPS may include multiple visits, multiple truck rolls, a variety of parts, and other labor costs.
Some organizations may measure Cost Per Work Order, but that metric leaves out cases that include always assigning experts to the most complex (and expensive) jobs. Additionally, it does not account for cases where multiple work orders are related to the same core issue.
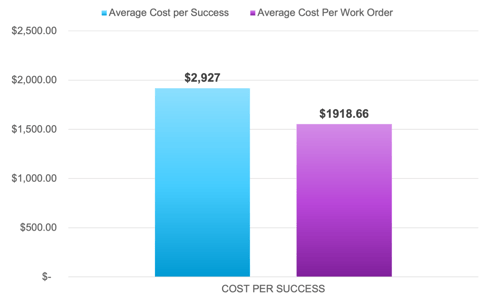
Key Observation:
Successfully resolving an issue involves nearly 42% more in costs versus looking at work orders individually. While average costs are dependent on the company and type of equipment being serviced, the cost difference is the most important to keep in mind.
MTTR - Mean Time to Resolution
What is it?
The Mean Time to Resolution KPI measures the time it takes to resolve a customer issue. Typically, it’s the time between the case creation date and the closure date. Similar to the pain of staying on hold when trying to resolve a personal issue, minimizing MTTR is a key factor in increasing positive customer experiences and reducing service costs. In the last year, we’ve seen a growing divide in this metric.
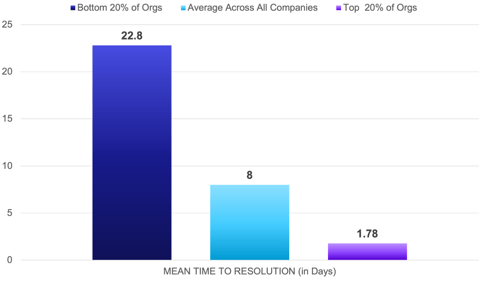
MTTR (in days):
• 8 days: average across all companies• 1.78 days: top 20% of organizations• 22.8 days: bottom 20% of organizations
MTBF - Mean Time Between Failures
What is it?
Mean Time Between Failures quantifies the average time between customer issues. Service organizations try to maximize this metric because a higher rate represents excellent service quality and maximum uptime.
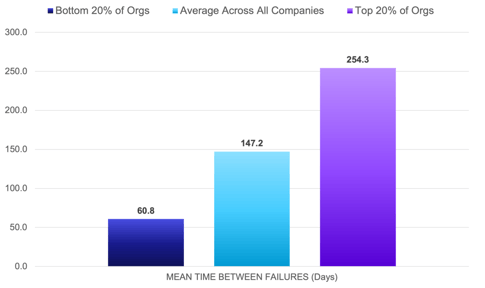
• 139.9 days: Average across all companies (147.2 in 2021)
• 231.8 days: Top 20% of organizations (254.3 in 2021)
• 57.5 days: Bottom 20% of organizations (60.8 in 2021)
Key Observation:
Individual pieces of equipment may have differing life cycles, but service leaders need to understand underlying patterns—in both their machines and workforces. When visiting a job site, experienced service heroes know how to use their time wisely and ensure that assets are working properly before leaving. This can significantly extend the time between failures.
MTBV - Mean Time Between Visits
What is it?
Need to calculate both uptime and service performance? Look no further than the Mean Time Between Visits metric. This measures every visit you have for an asset or customer, instead of only tracking time between failures.
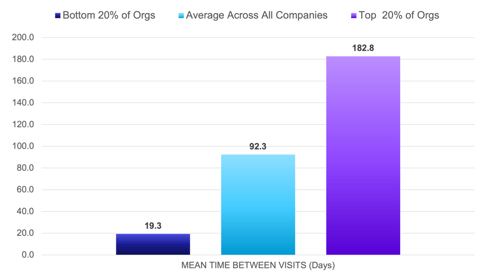
• 92.3 days: average across all companies
• 182.8 days: top 20% of organizations
<• 19.28 days: bottom 20% of organizations
Key Observation:
Experienced techs will skew towards longer time intervals between visits. That’s great news, thanks to low repeat visit rates, as well as their ability to utilize every visit to maximize uptime.

This feature is just one short excerpt from a report published by Aquant.
www.fieldservicenews.com subscribers can read the full report now by hitting the button below.
If you are yet to subscribe you can do so for free by hitting the button and registering for our complimentary subscription tier FSN Standard on a dedicated page that provides you instant access to this white paper PLUS you will also be able to access our monthly selection of premium resources as soo as you are registered.
 Data usage note: By accessing this content you consent to the contact details submitted when you registered as a subscriber to fieldservicenews.com to be shared with the listed sponsor of this premium content Aquant who may contact you for legitimate business reasons to discuss the content of this white paper, as per the terms and conditions of your subscription agreement which you opted into in line with GDPR regulations and is an ongoing condition of subscription.
Data usage note: By accessing this content you consent to the contact details submitted when you registered as a subscriber to fieldservicenews.com to be shared with the listed sponsor of this premium content Aquant who may contact you for legitimate business reasons to discuss the content of this white paper, as per the terms and conditions of your subscription agreement which you opted into in line with GDPR regulations and is an ongoing condition of subscription.
Further Reading:
- Read more about Aquant on Field Service News @ www.fieldservicenews.com/aquant
- Read more about Digital Transformation @ www.fieldservicenews.com/digital-transformation
- Read more about Leadership & Strategy @ www.fieldservicenews.com//leadership-and-strategy
- Learn more about Aquant @ www.aquant.io
- Follow Aquant on Twitter @ twitter.com/Aquant_io



















 Field Service News is published by 1927 Media Ltd, an independent publisher whose sole focus is on the field service sector. As such our entire resources are focused on helping drive the field service sector forwards and aiming to best serve our industry through honest, incisive and innovative media coverage of the global field service sector.
Field Service News is published by 1927 Media Ltd, an independent publisher whose sole focus is on the field service sector. As such our entire resources are focused on helping drive the field service sector forwards and aiming to best serve our industry through honest, incisive and innovative media coverage of the global field service sector.
Leave a Reply