AUTHOR ARCHIVES: Mark Glover
About the Author:

Mark is an experienced B2B editor and journalist having worked across an array of magazines and websites covering health and safety, sustainable energy and airports.
Jun 04, 2019 • Fleet Technology • News • Geotab • fleet
Geotab have announced the availability of two new mobile workforce management solutions by Actsoft, Inc. on the Geotab Marketplace.
Helping business to streamline processes and gain greater visibility into drivers and assets, Encore and Workforce Manager by Actsoft, are the latest solutions to join the Marketplace’s growing portfolio of mobile apps, software Add-Ins and hardware Add-Ons that enable Geotab customers to better manage their fleets.
Encore, Actsoft’s flagship product, enables companies to maximize efficiency in daily operations, providing businesses with the dynamic tools necessary to effectively oversee and engage remote employees and assets when in the field. Offering a wide range of functionality, such as mobile timekeeping, wireless forms and GPS-based tracking, Encore helps to streamline current processes, allowing fleet managers to benefit from more accurate workforce data and minimize discrepancies. Workforce Manager is a nearly identical software, but is exclusive to AT&T customers.
“We’re very excited to embark on this new journey in collaboration with Geotab,” said Kevin Thigpen, Chief Operating Officer at Actsoft. “The Geotab Marketplace, with its vast hub of telematics innovations, is the perfect home for Actsoft and its increasing portfolio of GPS-enabled workforce management solutions.”
As an industry leader in mobile resource management, Actsoft has been providing solutions to help businesses achieve their maximum potential for over 20 years. It’s award-winning suite of software tools for improved worker and asset management, is utilized by thousands of customers around the globe to power data-driven decision making. Joining over 150 partner solutions on the Geotab Marketplace, Actsoft’s Encore and Workforce Manager solutions are available to the more than 40,000 Geotab customers who are leveraging telematics data to better manage their fleets.
“The Geotab Marketplace is designed to help businesses customize their telematics solution and utilize vehicle data to increase the overall efficiency of their fleets, ” added Joey Marlow, Executive Vice President, U.S. Operations at Geotab. “The perfect complement to our Marketplace, Actsoft and its solutions provide customers with an all-encompassing workforce management solution that further strengthens any fleet-based operation, helping businesses become more productive today and into the future.”
Jun 04, 2019 • Features • 3D printing • manufacturing • Additive Manufacturing • Parts Pricing and Logistics
An industrial products manufacturer has a large portfolio of spare parts in its portfolio. It has 10 year service contract with its customers implying that the company must be able to deliver spare parts on time for 10 years to its customers even though the product may longer be produced. Thus, the company has to maintain inventory of some of those spare parts. Such inventory costs run into millions of dollars. Many of those spare parts are produced by suppliers. Demand for those spare parts are low and unpredictable.
On Monday morning, the spare parts manager received a call from a customer in another continent “ Mr. Paul, our equipment is out of action as it cannot be started in the morning shift. My maintenance guys confirmed we need to replace a part, supplied by you and we do not have it in inventory. I am sending you the part number. Please deliver it within three days otherwise there will be heavy loss.” Mr. Paul checked the part number in the ERP and found that they also do not have in stock.
He found out who the supplier is and called him up. The supplier replied saying that they cannot make only one piece. They will need an order size of at least 20 and it will take 1 week. What will Mr. Paul do? He remembered that the Vice President (VP) of Supply Chain was talking about 3D Printing of spare parts in the last meeting. Can the part be printed? How will Mr. Paul figure that out?
He refers to the presentation by VP- Supply Chain and finds the name of a company called 3D Hubs (UPDATE: 3D Hubs is now Hubs). Mr. Paul checks out the website of 3D Hubs and found that he can upload the drawing of the parts and get an analysis for printability along with a quote. He uploaded the drawing, got the quote for delivery within three days and went to his boss.
His boss, Mr. James said “Are you crazy? How will I be able to justify that price? Also, have you noticed that they are not printing our part using our specified material? This will never work.” Mr. Paul tried to argue “This is a very strategic customer for us. If they are not satisfied and cancel the service contract, it will be a big trouble for us. We can say that they can run their equipment with it until an actual replacement spare part is produced and delivered by the supplier. I can talk to R&D about the approval for the deviation in material. It doesn’t seem to be a big change.” Mr. James said “You are taking a big risk, Paul. If you want to try, go ahead.”
In the end, everything turned out well. That part was produced using additive manufacturing (AM) and delivered on time. Paul received appreciation for his efforts. VP- Supply Chain was very happy and said to Paul. “Now, I want to evaluate our entire spare part portfolio and develop a systematic process of evaluating which of those parts can be printed and which cannot. It will be great if you can evaluate our portfolio and present in our next month’s meeting.”
Paul has 10 years of experience in spare parts but he does not know much about 3D Printing. How can we help Paul? I am sure that there are many people like Paul in large industrial manufacturers, who need similar help. Lets try to outline a steps-by-step process for selecting spare parts suitable for additive manufacturing.
Step 1: Identify the objectives
Some potential objectives for producing spare parts using AM can be:
• Supply risk reduction;
• Lead time reduction;
• Inventory cost reduction;
• Ensuring local content;
• Minimizing loss of production;
• Reducing carbon foot print across life cycle.
Companies can decide the most relevant ones from those and provide relative importance of those using a method called analytic hierarchy process. Instead of directly assigning importance weights to each objective, experts within the company can make pairwise comparison of the objectives using a scale (for example 1-3-5-7-9) and derive the importance weights.
Step 2: Identify the factors to be used for screening the spare parts for AM suitability
Some factors, which can be used for screening the spare parts for AM suitability can be as follows: It is important to note that the company should have data on the following factors to be considered for screening.
If such data is not available or available in different IT systems or in physical form ( i.e. drawings with dimensions and material specifications), it will be difficult to include those at the screening stage.
1)Demand and demand uncertainty of the parts
Parts with low and uncertain demand are more suitable for spare parts
2) Overall part size
(Part must fit build volume of the equipment) As the equipment for different AM technologies have build size restrictions, part-size is usually a restriction, if it cannot be fitted in the build chamber. Sometimes changing the orientation of the part may be needed to fit it into the build chamber, but it might require additional support structures and may increase the overall production time. Decisions about part orientation in the build chamber can be taken only for the selected parts and not at this stage. The company can specify the upper limit of size or a range of sizes of parts, which they would like to consider
3) Materials
Not every material can be printed. Thus, parts whose specified materials can be printed can be screened when a company is starting on its journey of producing spare parts using AM. Later, alternate materials which closely match the specifications can be explored.
4) Supply lead time
Parts with long supplier lead time for conventional manufacturing can be more suitable for producing using AM as overall lead time can be reduced. A company may decide to specify either the lower limit or range of lead time, which they would like to consider.
5) Purchase price or unit cost
High priced parts, in general, can be suitable for AM but some high valued parts may be infeasible because of their size or materials etc.
6) Value of inventory across all locations
Usually parts with high inventory value can be good candidates to be produced using AM. High value of inventory can be due to high number of parts in stock or due to high prices. Sometimes, if a lot of stock is available, a company may decide not to proceed with producing such a part using AM. Some other company may decide that they would like to get rid of that stock and hence it may be worth producing those using AM. A company may also decide to include either price or inventory value as a screening factor.
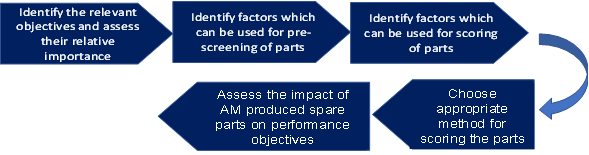
Figure 1: Step-by-step approach for selecting spare parts suitable for AM
Step 3: Identify the factors to be used for scoring the spare parts for AM suitability
Some potential factors for scoring spare parts in terms of their suitability for AM can be as follows:
• Lead-time;
• Unit cost;
• Criticality in terms of influence of the part for equipment shutdown;
• Demand predictability measured as standard deviation of demand;
• Supply risk in terms of number of suppliers;
• Minimum order quantity.
The screened parts can be scored based on the above factors and how the factors are related to the objectives. Parts with long lead time, high cost, high criticality, low demand predictability, high supply risk and high minimum order quantity in the existing manufacturing process will be more suitable for AM.
Step 4: Choose appropriate method for scoring the parts
There can be multiple approaches to score the spare parts in terms of suitability to be produced using AM.
We mention some basic guidelines below:
1. Multi-criteria decision making approach (MCDM) –scoring parts on factors and linking factors to be objectives (suitable for less number of factors and less number of parts).
2. Logic decision diagrams, cluster analysis and fuzzy inference system (suitable for large number of parts, medium number of factors but strong interrelationships of factors and objectives). If the factors are dependent on each other and how they influence the objectives depends on the levels of the factors i.e. low, medium and high, logic decision diagrams can be built to score a part using different decision rules. In terms of disagreement between experts about the relationships, the relationships can be expressed as fuzzy numbers and fuzzy inference system can be used to score the parts.
3. Cluster analysis and MCDM approach for ranking of part clusters and within cluster ranking of parts (large number of diverse parts, limited to medium number of factors and independence of factors) If the factors considered are independent but the spare parts portfolio is very diverse, it will be necessary to cluster the parts, rank the clusters and then rank the parts within the clusters.
4. Bottom-up expert driven selection using a questionnaire or selection protocol (no data available or not possible to do quantitative analysis) If no data is available in digital form to score the parts, it is prudent to use the expert judgment of the service personnel or maintenance technicians. But, as those persons may not be aware of AM technologies, it is important to demonstrate to them what is possible using AM through workshops and ask them to suggest spare parts, which they find most difficult to get. Companies can also potentially run internal competitions to identify some spare parts to start with.
Step 5: Assess the impact of AM produced spare parts on performance objectives
Once some spare parts are identified, the next step is to develop business cases for the parts. But, those can be done once the appropriate technologies and equipments are identified. For that purpose, a database of all available AM equipments, the technologies they use, the materials they use, the build chamber of the equipments, the surface finish achievable need to be documented.
For the spare parts which are scored high in terms of their suitability for AM, the most appropriate technologies and equipments can also be shortlisted. Then total-cost of ownership based cost models need to be developed to understand the economic implication of producing the parts using AM. The relevant cists which need to be considered are materials, production, energy, labour as well as the savings in inventory and transportation costs over the lifecycle of usage of the parts for different demand scenarios.
Quotes from different service providers can also be used as a reference for taking the final decision. Once a company has done this exercise and identified a few feasible parts, some machine learning techniques can be used to identify the patterns amongst the most suitable parts so that the process can be automated when new parts are added to the portfolio.
Jun 03, 2019 • News • Automation • Comarch • Software and Apps
Managing tens of thousands of field service tasks per day in numerous locations requires enormous human resource capacity and generates significant costs. Additionally, with more than half a million network elements and thousands of employees engaged in the service delivery process, management of incoming issues is complex and time-consuming. MegaFon was looking to streamline these operations, minimize income losses resulting from network and service downtime, and improve field service quality. To reach those business objectives, Comarch implemented its Field Service Management system.
With the on-premises application of Comarch Field Service Management and the Comarch FSM Mobile app, the daily, paper-based responsibilities of engineers, managers and administrators have been digitized. In addition, subcontractors’ employees can now access the system and use its capabilities. As a result, field work management has been unified and centralized, which was crucial for the company.
Deployment of the software enabled MegaFon to automate field workforce management, optimize planning and scheduling, and introduce real-time reporting. With these features, the company is now able to manage tasks efficiently in connection with emergency incidents, planned works, customer complaints, energy systems and infrastructure problems from mobile and fixed networks.
“The implementation of the Comarch FSM solution in MegaFon is another opportunity to share our experience in the telecommunication sector and advise our client on how to optimize their processes. This project allowed us to build a strong presence on the Russian market,” says Szymon Uczciwek, Head of Field Service Management Consulting in Comarch.
About Megafon
MegaFon is one the leading telecommunication service providers in Russia, claiming 29.5% of the market share in 2017. The company and its subsidiaries operate in all Russian regions, along with Abkhazia, South Ossetia and the Republic of Tajikistan. Their subscriber base exceeded 77 million at the end of 2017.
Megafon’s company offer covers all telecoms market segments. Services include voice, mobile data, fixed-line telecommunication services, digital TV, IP telephony and innovative solutions such as mobile TV, OTT video content, M2M, mobile and financial advertising and cloud services.
MegaFon’s shares have been traded on the Moscow Stock Exchange since 2012, and on the London Stock Exchange since 2014.
About Comarch
Comarch is a global supplier of software and services for enterprises. It has over 20 years’ experience designing, implementing and integrating IT solutions for some of the world’s largest brands, including BP, Deutsche Telekom, Diageo, KPN, Orange, Telefónica, Unilever and Vodafone. Comarch has a specialist telecoms unit providing IT solutions to telecoms operators around the world. It builds technology solutions to meet the key requirements of telecoms companies, namely to increase revenue, grow business efficiency, simplify systems, cut costs, enhance the customer experience, build new services and shorten their time to market.
Comarch IT solutions for telecoms have been consistently listed in Gartner’s Magic Quadrant report, while its IoT offer has been evaluated positively by Berg Insight, IHS Markit and Gartner, who also named Comarch a “Vendor to watch” in the 2017 Market Trends: A Comprehensive Approach to CSP IoT Platform Selection Will Enhance Market Positioning.
The company has also been recognized for its work in the telecoms industry by other analysts, including Forrester, Informa and Frost & Sullivan.
Jun 03, 2019 • News • future of field service • Software and Apps • Microsoft HoloLens • mixed realities • HSO
Wearing a Mixed Reality headset, an engineer can share what they see and communicate with another engineer miles away. They might also be able to simultaneously call up manuals or other information through a heads-up display and view details provided by their assisting engineer.
Last month saw the launch of Hololens 2, the much-improved successor to Microsoft’s mixed reality headset Hololens. Microsoft is not a lone voice in the dark, with a plethora of other companies working on technologies with similar applications. Nreal and Zappar are just two of the start-ups trying to cash in on this emerging market. Are their investors just taking a gamble or are there good reasons for their investments?
This makes one wonder – is Mixed Reality just another gimmick or could it bring major benefits to Field Service operations? I suspect the latter, and here is why:
The adoption of new technologies tends to follow the S-Curve. As a product or technology gains traction in the market, its market begins to grow. At first, the growth is slow, almost imperceptible. It then develops more rapidly as consumers begin to adopt the technology. As the market expands, that growth continues. Finally, a host of factors cause the growth rate to decline and then gradually growth tapers off as it becomes a replacement market.
"The adoption of new technologies tends to follow the S-Curve..."
So where is Mixed Reality on the S-Curve? In his much quoted “Diffusion of Innovation”, Everett Rogers terms the first group to adopt a new technology as “Innovators”. Innovators are characterised by a willingness to take risks, have the highest social status, have financial liquidity and have closest contact to scientific sources and interaction with other innovators. Their risk tolerance allows them to adopt technologies that may ultimately fail. Financial resources help absorb these failures. I would suggest that the US military, who have just placed a large Hololens order, fits squarely into this category.
The next stage of adoption belongs to the early adopters. Early adopters have a high degree of opinion leadership as well as high status and financial liquidity. Whilst facts and figures are still sparse, anecdotal evidence suggest that we may already have started to move into this phase. The companies I hear about who are investigating Mixed Reality are in niche markets, very profitable and their engineers are highly skilled. They are happy to take some risks and try innovative solutions. This suggests that we may be about to accelerate fast up the S- Curve, but what benefits can we expect?
Well, wouldn’t it be nice if we could bottle skills and experience. Unfortunately, this isn’t the case and wherever we look we encounter skills shortages. Be it HVAC, Gas Central Heating or High-Speed Printing; in Cornwall, London or Scotland – companies struggle to recruit experienced engineers. In niche sectors it is the worst. When baby boomer engineers are retiring they the take their skills with them and it’s hard to replace them. Would it not be great if a senior engineer could guide the engineer on site through fault-finding and repair from the comfort of the office (or even from home), in real time? How many senior engineers could you retain this way?
But then, do we need to stay with the traditional model of service visits. In many sectors it is common that the first visit is about identifying the fault and the parts required to fix it. We may try to do this over the phone but often without success. How often could this be done by customer staff with guidance from a skilled engineer delivered remotely via Mixed Reality? I imagine it would be a lot, if it was easy enough. How much would that improve engineer productivity and first-time-fix rates and fix-times? And what about inaccessible locations or when the fault occurs off-shore or on a ship? The benefits of Mixed Reality for fault finding and assisted repairs are massive. Of course sometimes it’s as simple as getting a second opinion about a tricky issue.
Then there is training. Ever simulated a fault and waited forever whilst six trainees take turns resolving it with their heads in a confined space? Wearing Mixed Reality headsets, they could be right there with the trainer inside the machine.
These are just a few examples. As technologies expand and become cheaper, their applications multiply. Just think what you could do with a mobile phone 10 years ago and what we use it for now. No wonder some industry analysts expect shipments of Mixed Reality devices to exceed five million in the next three years.
So, yes – I see Mixed Reality changing the way we do service, and soon!
Danny Wieder is a Field Service Consultant at HSO.
Jun 03, 2019 • News • future of field service • IIOT • Blockchain • Cyber Security • Software and Apps • IoT Security
SigmaDots blockchain-based solution enables protection for IoT and IIoT systems.
SigmaDots blockchain-based solution enables protection for IoT and IIoT systems.
SigmaDots, a cyber-security startup and subsidiary of Essence Group, has partnered with Telit, a global enabler of the Internet of Things (IoT), to expand IoT security and strengthen business continuity leveraging SigmaDots technology. Essence Group is a market leader in developing LTE-based connected devices and IoT platforms.
SigmaDots has developed the first embedded, blockchain-based cybersecurity solution for IoT and IIoT systems. Telit, recognizing the need for enhanced solutions, is working closely with SigmaDots to improve resilience to cyberattacks. The companies are collaborating on the use of blockchain technology for routers, control panels, IoT gateways, and a host of IoT devices, drastically reducing device vulnerability to cyberthreats.
“The ubiquity of IoT devices makes them attractive targets for cyber mischief,” said Alon Segal, SVP of Software & Services, Telit. “Our collaboration with SigmaDots adds another layer of security and communications resiliency using distributed technologies to offer advanced, secure infrastructure solutions for our customers.”
SigmaDots software-based solutions harness the power of serverless architecture, bringing blockchain-based cybersecurity to the IoT ecosystem. With a scalable, interoperable, and secure platform uniquely adapted to the limited resources of IoT, SigmaDots empowers connected ecosystems to accelerate the machine-to-machine economy.
“IoT is finally delivering on its promises of complete connectivity – wearables, mobile apps, home safety, smart meters and in industry – generally anywhere” said Itsik Harpaz, General Manager of SigmaDots. “However, this connectivity brings significant threats – an attack on a single device can spread throughout the entire network.”
IoT devices without strong cyber protection can easily become part of a botnet to carry out distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks or fall prey to IoT-focused attacks like man-in-the-middle, data and identity theft, and device hijacking.
“SigmaDots technology was developed out of the need to strengthen the security of our IoT devices,” said Dr. Haim Amir, CEO and founder of Essence Group. “We’ve been creating innovative connected device solutions for more than 25 years, so we fully understand the challenges and the necessity of creating airtight cyber protection.”
May 31, 2019 • Features • consumer electronics • Mike Pullon • Hardware • Rugged devices • The Field Service Podcast • Varlink
In the latest Field Service Podcast, Mike Pullon discusses if rugged devices will ever be replaced by their consumer cousins.
In the latest Field Service Podcast, Mike Pullon discusses if rugged devices will ever be replaced by their consumer cousins.
With the boundaries of consumer and rugged becoming more blurred, we spoke to Mike Pullon, CEO and Founder of Varlink - an outfit that distributes specialist rugged devices - if high-street phones and tablets will ever replace their rugged counterparts.
May 31, 2019 • News • BigChange • cloud • Software and Apps • Waste Management
Established for 50 years, Thetford International is a founder member of CHEM, the Container Handling Equipment Manufacturers Association. The company has become a market leader in the design and manufacture of all types of compaction equipment, supplying to a diversity of sectors, from the print industry and supermarkets to industrial complexes, recycling centres and refuse transfer stations.
Thetford uses JobWatch, the BigChange solution for managing mobile service operations using live-connected mobile devices running a multi-functional app to replace all paperwork, integrated with vehicle tracking to monitor the fleet and drivers. As well as replacing nine A4 carbon-copy installation and service forms, the JobWatch 5 in 1 app is also used for engineer time sheets, risk assessments, driver vehicle checks and the management of parts.
Thetford carries out routine maintenance of compactors but the majority of work is reactive and requires a fast response due to the safety concerns of potentially dangerous equipment. Job details are sent to the assigned engineer to complete with JobWatch managing the entire process from start to job completion.
“We had been on the lookout for a suitable system for a numbers of years but nothing seemed to exist that really combined the tracking and field service reporting needs,” says Andrew Goddard, Service Manager, Thetford International. “The BigChange solution is very flexible and adaptable and we were able to tailor it to meet our needs.”
JobWatch has been integrated with Thetford’s own bespoke IT system called Onsite providing asset register synchronisation and the seamless interchange of data between the systems. According to Thetford, the biggest benefits are financial and in particular with regard to invoicing.
“Previously it could take up to 3 weeks to raise an invoice. Now we do it next day and potentially we could do it the same day,” explains Goddard. “JobWatch ensures invoices are accurate and are in line with what the customer is expecting and as they are received soon after the job, there are many fewer queries and payment is always quicker.”
Thetford’s engineers cover the UK working from their homes. With vehicle tracking fitted to the fleet of Ford Transit vans, BigChange provides an automated ‘clocking in and clocking out’ system. With van often stocked with thousands of pounds of parts, it also offers added security and driver monitoring and rating has also encouraged safer driving; important as engineers travel as much as 40,000 miles a year.
JobWatch has also been developed to manage Thetford’s stock control with engineers using their tablets to record parts used. With around 400 individual parts, the system automatically replenishes stocks with deliveries to engineer collection points.
“Previously the vast majority of information was held in people’s heads and by introducing BigChange we have brought all that knowledge into one place. It all works very well and seamlessly with our other systems. The whole service operation just runs a lot more smoothly and our customers – and the company Accountant – are a lot happier!” Goddard adds.
May 30, 2019 • Features • future of field service • WBR • field service asia
WBR Asia’s Wendy Zheng, explains why the Asia Pacific region has become a hot bed of field service innovation...
WBR Asia’s Wendy Zheng, explains why the Asia Pacific region has become a hot bed of field service innovation...
Field service is on an upward trajectory all over the world, and one region is leading the charge to challenge the US dominance of the industry. The worldwide market size of the field service management industry is expected to grow to $5.08 billion by 2023, with a compound annual growth rate of 14.7%.
This growth is being driven, in part, by the onslaught of innovative new technology which is making the whole industry more efficient and cost effective. Mobile applications, wearable devices, cloud hosting, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are all helping field service engineers and the administrative staff who support them to deliver superior customer experience.
However, while North America still holds, and is expected to continue holding, the largest market share, the Asia Pacific region is predicted to exhibit the most rapid rate of growth during the period. With the increase in the number of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) in the emerging countries, such as China and India, competition in APAC is expected to grow at a because of automation in various business processes, including job scheduling, billing and invoicing, and service delivery.
Asia Pacific
One reason for this rapid rate of growth is attributed to the fact of the emerging markets of the region (such as India and China) being home to a large number of small and medium sized enterprises.
The continued increase in the number of these enterprises leads to a sympathetic increase in competition. This, in turn, drives the introduction of innovative technology, such as automation for various business processes such as job scheduling, billing and invoicing, and service delivery.
“Asia Pacific is expected to witness the highest CAGR in the global field service management market during the forecast period,” writes Globe Newswire. “This is primarily due to large-scale industrialization in Asian countries such as China, India, and Japan. With enhanced geographic zones and a high client base, the Asia Pacific region is expected to exhibit a strong growth in the field service management market. Increasing number of technology users in Asia Pacific region further propels the growth of field service management market in this region.”
Competition has always driven innovation as individual companies try and outdo one another in the eyes of their clients. It’s the same reason why the greatest leaps forward in technology occur during times of war, with the business world being just as susceptible to an arms race as the military can be.
Cloud Field Service Management
One of the new technologies which is particularly helping the Asia Pacific region grow at a rapid rate is the adoption of cloud-based field service management systems.
Cloud-based field service management solutions continually harvest and archive data, allowing businesses to use the resultant historical archives to identify trends and patterns and improve the necessary processes, leading to a better customer experience.
For example, it could be identified via automated cloud-based field service management tools that a certain part or component seems to have a recurring fault. Once this has been identified the manufacturer of the component can be contacted so they can make the necessary design changes, or the field service company can change to a different provider.
Likewise, data can help identify factors which are leading to field service engineers making wasted journeys or becoming delayed. Changes can then be made to scheduling or work shifts to make sure the right people are always in the right place, at the right time. Similarly, when it comes to spare part stock control, if a particular item is shown to regularly run low, purchasing can be adjusted as necessary.
Final Thoughts
The Asia Pacific region is leading the way in adopting this kind of cloud-based technology. It is technology such as this, combined with the competition being driven by the increase in small and medium sized enterprises, which is helping these emerging countries take the fight to North America as the new hot contender in the global field service marketplace.
“There is increasing demand to increase productivity and reduce operating costs,” writes IT Tech Herald. “Players are adopting field service management solutions to enhance customer experience, with customer demands and the logistics of managing field teams continuing to increase in complexity. Emergence of new technologies such as IoT and mixed labor models are promoting the market growth. Thus, increasing demand to enhance productivity and advent of various technologies are anticipated to drive the market growth during the forecast period.”
Asia’s position as the up and coming new stage for field service is sure to be a hot topic at Field Service Asia 2019, Asia’s Leading Conference for Service, Support and Customer Care on 12-14 November, at the Amara Sanctuary Resort, Sentosa, Singapore.
May 30, 2019 • News • Artificial intelligence • future of field service • Machine Learning • Software and Apps • utilities • inawisdom
By utilising the latest Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) tools from AI innovators, Inawisdom and Amazon Web Services (AWS), Drax Group has transformed its data insight and customer intelligence to personalise the services it provides to its customers, through its B2B energy supply businesses Opus Energy and Haven Power.
As a leading light in the renewable energy market, Drax Group is passionate about providing innovative and sustainable solutions for customers and has a mission to enable a zero carbon, lower cost energy future. As part of this initiative, Drax wants to identify any anomalies in energy usage, to help demonstrate to customers that it really understands how they’re using their electricity. Drax Group partnered with Inawisdom to deploy state-of-the-art Artificial Intelligence across its data and has since been able to provide a much higher standard of customer service.
“Our relationship with Drax Group has been a success story from the start,” said Neil Miles,CEO and co-founder of Inawisdom. “The utility sector is one of our core industries where AI and ML is proving a powerful instrument. Together with AWS, we were able to use our rapid deployment model to quickly find the real value in the data Drax held and help it to achieve goals effectively and efficiently”.
“Our partnership with Inawisdom and AWS has enabled us to draw insight and intelligence from our data, which was previously too complex to see,” reported Bjoern Reinke, Smart Director from Drax Group. “We can now immediately identify unusual usage and respond accordingly, providing many benefits for our customers and in turn Drax Group’s B2B supply businesses. The speed this capability has been provided is a revelation”.

















 Field Service News is published by 1927 Media Ltd, an independent publisher whose sole focus is on the field service sector. As such our entire resources are focused on helping drive the field service sector forwards and aiming to best serve our industry through honest, incisive and innovative media coverage of the global field service sector.
Field Service News is published by 1927 Media Ltd, an independent publisher whose sole focus is on the field service sector. As such our entire resources are focused on helping drive the field service sector forwards and aiming to best serve our industry through honest, incisive and innovative media coverage of the global field service sector.
Leave a Reply